Weigert-Meyer law
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
View The Radswiki's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Weigert-Meyer rule
- Meyer Weigert rule
- Stephen's ectopic pathway
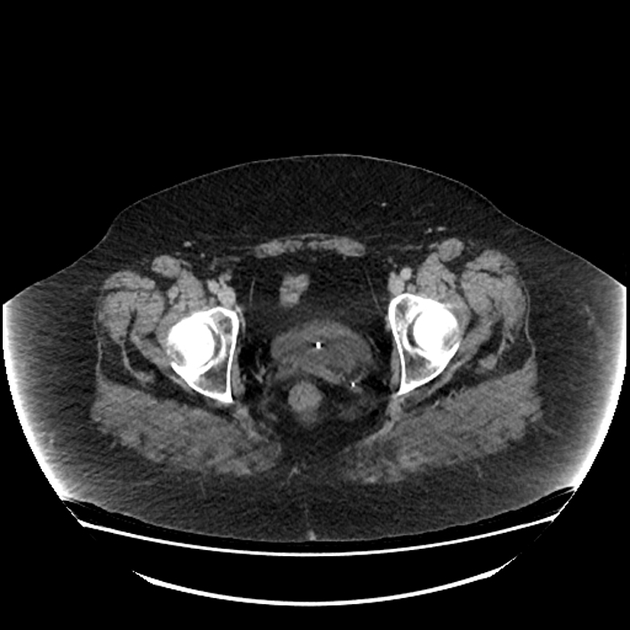
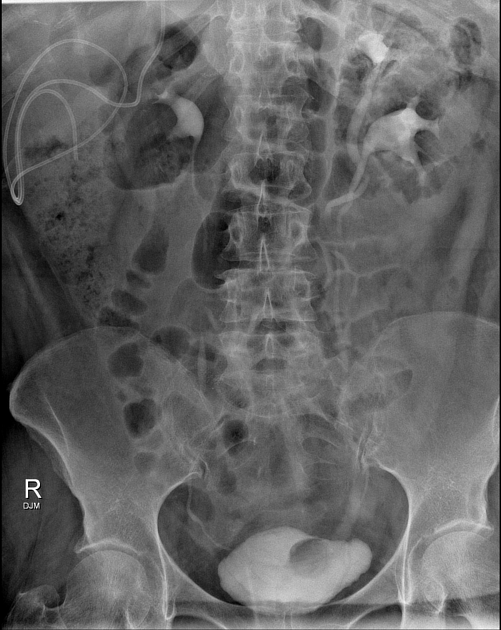
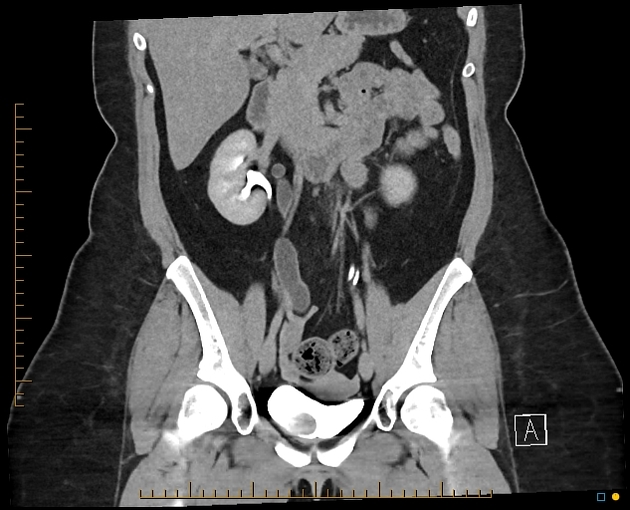
The Weigert-Meyer law describes the relationship of the upper and lower renal moieties in duplicated collecting systems to their drainage inferiorly.
On this page:
Weigert-Meyer law
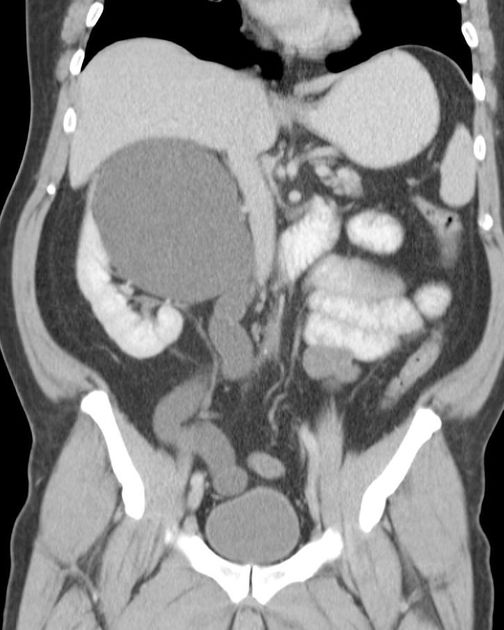
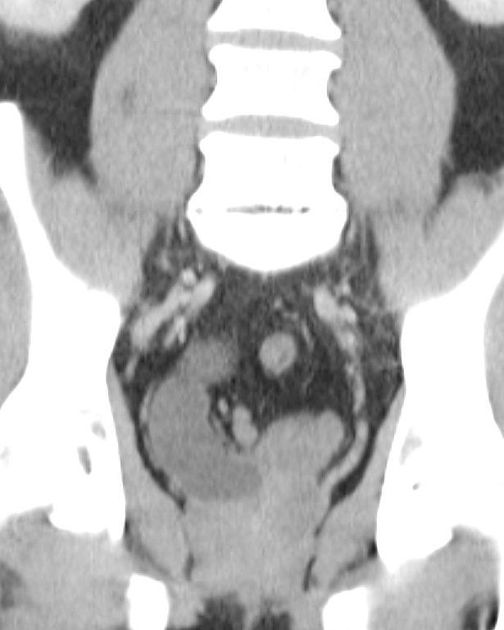
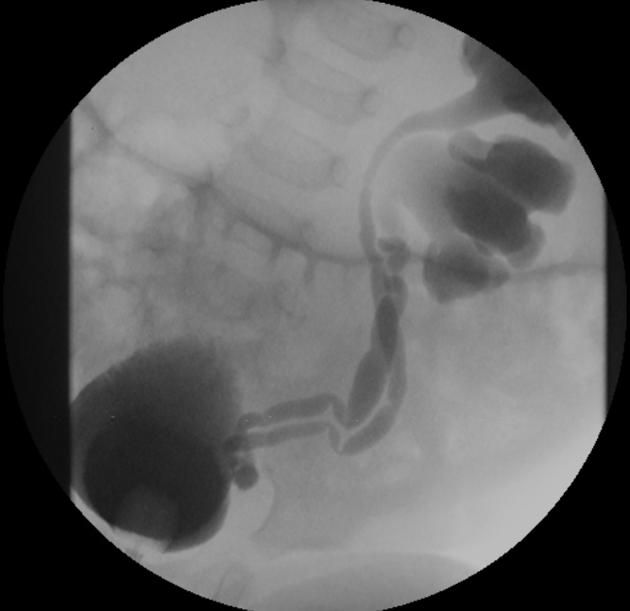
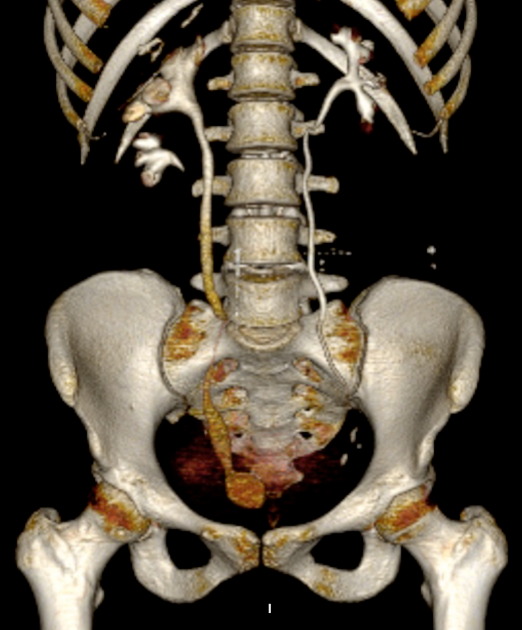
With duplex kidney and complete ureteral duplication, the upper renal and lower renal moieties are drained by separate ureters, each having its own ureteral orifice in the bladder.
upper renal moiety ureter has ectopic insertion medial and inferior to the lower renal moiety ureter, and frequently ends in a ureterocele
lower renal moiety ureter has orthotopic insertion lateral and superior to the upper renal moiety ureter, and vesicoureteral reflux can occur
Embryologically, duplication occurs when two separate ureteric buds arise from a single Wolffian duct (mesonephric duct). Due to the future lower pole ureter separating from the Wolffian duct earlier, it migrates superiorly and laterally as the urogenital sinus grows and becomes the upper pole moiety. Despite this migration of the upper tract, the insertion inferiorly maintains the original embryologic relationship, and thus the upper pole moiety ureter drains infero-medial to the normal lower moiety ureter.
The ectopic insertion often has a ureterocele which obstructs its own collecting system, and can distort the orthotopic lower pole moiety insertion such that it is prone to reflux.
Stephen's ectopic pathway
As always, there are exceptions to the rule. Rarely reported in the literature, Stephen's ectopic pathway postulates that an ectopic ureter may drain not only distally to the normal ureteric orifice (as per Weigert-Meyer law), but may drain medially and superiorly to it (breaking Weigert-Meyer law) 6,7.
History and etymology
Carl Weigert (1845-1904) was a German pathologist who published his findings regarding ureteric duplication in 1877 8,9. Robert Meyer was an American pathologist who first published on this subject in 1907 and formulated it as a "rule" in 1946 5,10.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Glassberg K, Braren V, Duckett J et al. Suggested Terminology for Duplex Systems, Ectopic Ureters and Ureteroceles. J Urol. 1984;132(6):1153-4. doi:10.1016/s0022-5347(17)50072-5 - Pubmed
- 2. Callahan M. The Drooping Lily Sign. Radiology. 2001;219(1):226-8. doi:10.1148/radiology.219.1.r01ap01226 - Pubmed
- 3. Sheth S & Fishman E. Multi-Detector Row CT of the Kidneys and Urinary Tract: Techniques and Applications in the Diagnosis of Benign Diseases. Radiographics. 2004;24(2):e20. doi:10.1148/rg.e20 - Pubmed
- 4. Weigert C. Über einige Bildungsfehler der Ureteren. Virchows Archiv für pathologische Anatomie und Physiologie und für klinische Medizin, Berlin, 1877, 70: 490.
- 5. Meyer R. Zur Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte der Ureterverdoppelung. Virchows Archiv für pathologische Anatomie und Physiologie und für klinische Medizin, Berlin, 1907, 87: 408.
- 6. Ganz A, Roloff J, Walz P. Der “Ectopic Pathway” - Fakt Oder Fiktion? Aktuel Urol. 1996;27(06):419-21. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1055631
- 7. Gregory T. MacLennan. Hinman's Atlas of Urosurgical Anatomy. (2012) ISBN: 9781416040897 - Google Books
- 8. Carl Weigert (1845-1904). JAMA. 1964;189(10):769-70. doi:10.1001/jama.1964.03070100063018 - Pubmed
- 9. Pioneers in Pathology. (2017) ISBN: 9783319419961 - Google Books
- 10. Meyer R. Normal and Abnormal Development of the Ureter in the Human Embryo?a Mechanistic Consideration. Anat Rec. 1946;96(4):355-71. doi:10.1002/ar.1090960403 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Bilateral duplex kidneys and collecting system
- Duplex collecting system with intravesical ureterocele
- VUJ calculus in ureterocoele
- Cecoureterocele containing a calculus
- Duplicated collecting system
- Duplex renal collecting system
- Duplex collecting system
- Bilateral duplex collecting systems
- Ectopic ureter insertion into the prostatic urethra
- Ectopic ureter insertion into vagina
- Duplex kidney
- Renal duplication with ureterocele (Weigert-Meyer rule)
- Weigert-Meyer rule illustration
- Renal duplication with obstructed upper renal moiety (Weigert-Meyer rule)
- Bilateral duplex kidney
- Incomplete double ureter
- Duplex kidney and ureterocele
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- coeliac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.