Presentation
Disturbed level of consciousness.
Patient Data
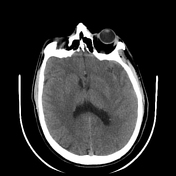



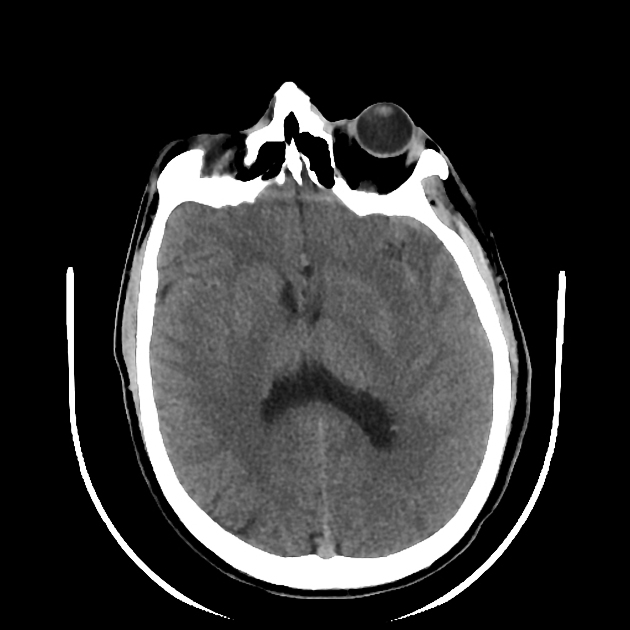
The CT study shows left temporal large cortical and subcortical patchy hypodensity.

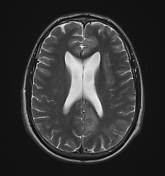

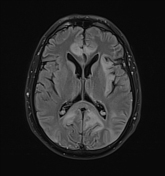

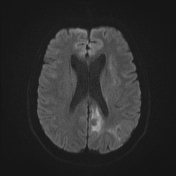

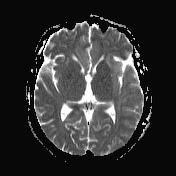

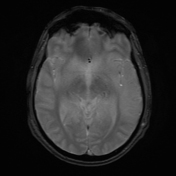

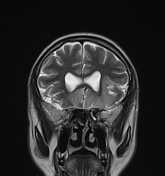

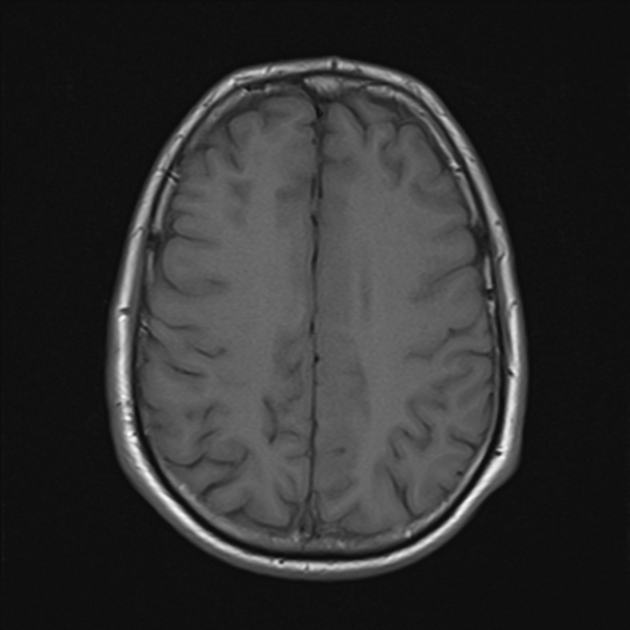
The MRI study shows the following:
bilateral asymmetrical involvement of the limbic system, temporal lobes, insular cortices, and inferolateral frontal lobes; the left posteromedial thalamic region is probably involved
the affected areas show generalized edema elicits a low signal in T1 and high signal in T2 and FLAIR
most of the affected regions show no restriction in the diffusion study with occasional T2 shine through, consistent with vasogenic edema
small regions show true restriction especially those at the bilateral posterior temporal (more left) as well as the left cingulate gyrus consistent with cytotoxic edema
no evidence of hemorrhagic changes in the T2 GRE
the basal ganglia is spared
Case Discussion
While the CT is reasonably matching with a left middle cerebral artery territory infarction, the clinical presentation did not completely fit given the patient presented with coma and fever with no lateralizing neurological deficits.
The MRI is typical for herpes simplex encephalitis confirmed with the molecular detection of herpes simplex virus 1 & 2 (PCR) in CSF.
Herpes simplex encephalitis is occasionally associated with cerebrovascular complications either hemorrhage or infarction. The hemorrhagic complications are associated with type 1 secondary to vessel disruption. The ischemic complications are associated with type 2 secondary to multifocal vasculitis 1.
This case shows areas of cytotoxic edema suggestive of ischemic changes.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.