Presentation
Discharging sinus opening at right side of neck since birth.
Patient Data
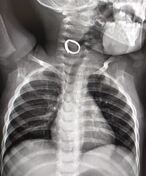
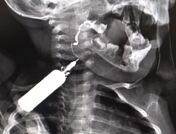
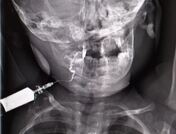

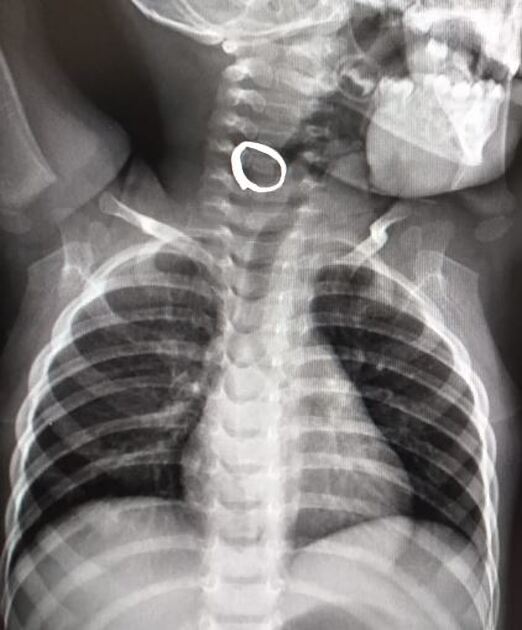
Contrast delineates a smooth convoluted track extending from a clinically visible opening on the right side of the neck close to the level of the hyoid bone upward to the level of mouth/right palatine tonsillar region and opacifying esophagus due to swallowing, corresponding to branchial cleft anomaly most likely second branchial cleft fistula.
Case Discussion
Brachial cleft anomalies include cyst, fistula and sinus. Cyst has no internal or external communication, fistula communicates both internally and externally while the sinus is a blind tract.
Second branchial cleft anomalies are by far the most common branchial anomaly. However, the second branchial cleft fistula is rare and account only 2% of all branchial anomalies.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.