Presentation
Head trauma.
Patient Data
Age: 50 years
Gender: Male
From the case:
Subdural hygroma


Download
Info
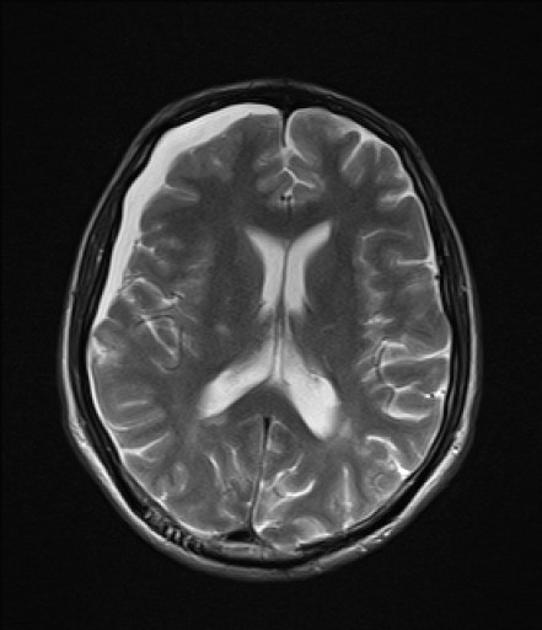
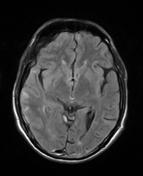
T2WI: An extra-axial collection with CSF signal intensity and the mild mass effect is seen in the right hemisphere.
FLAIR: Areas of high signal intensity representing SAH are seen in the sulci of the right temporal lobe.
Case Discussion
Differential diagnoses include subdural hygroma, chronic subdural hematoma, and cerebral atrophy. The presence of mild sulcal effacement and mass effect makes the diagnosis of brain atrophy less likely.
Due to the acute nature of trauma according to the patient description, acute traumatic subdural hygroma is more likely.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.