Presentation
Headache,nausea & vomiting , Prior CT study revealed sellar mass, for further evaluation.
Patient Data


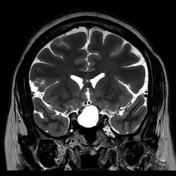

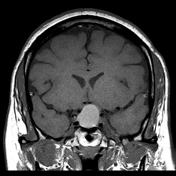

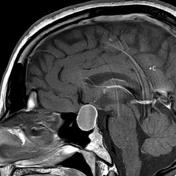

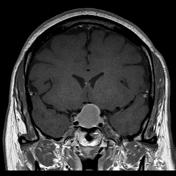

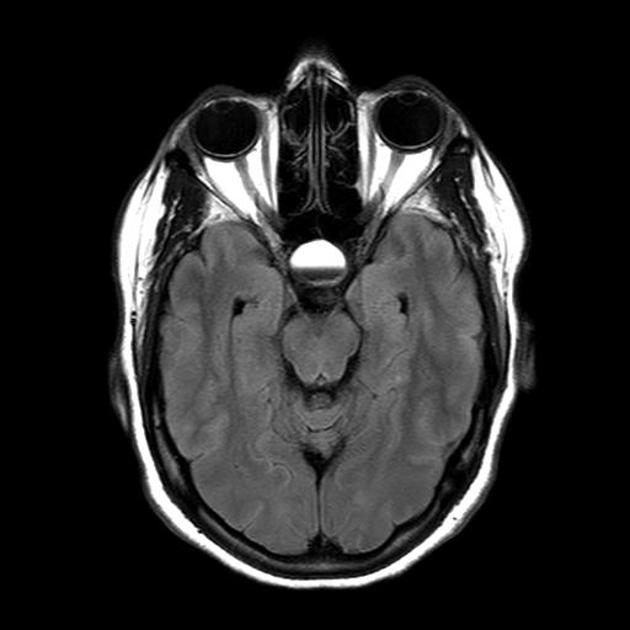
An ovoid mass lesion is seen in the pituitary fossa with suprasellar extension.The optic chiasm is markedly compressed, draped over the superior aspect of the mass lesion, sagging of the sellar floor is also noted encrocahing upon the sphenoid sinus with intra-sinus extension,
The mass is T1 and T2 hyperintense centrally showing blood-blood fluid level and mild marginal post contrast enhancement. No calcifications. A small solid component is located laterally (at the left cavernous sinus) and this component enhances.
Case Discussion
Diagnosis confirmed by radiological MRI features, No biopsy was obtained.
Pituitary apoplexy is an acute clinical syndrome caused by either hemorrhage or infarction of the pituitary gland . Although variable, it typically comprises of headache, visual deficits, ophthalmoplegia, and altered mental status . An existing pituitary macroadenoma is usually present (60 - 90%) but it can occur with healthy glands in few isolated cases.
Pituitary apoplexy may also occur during pregnancy or post partum period (Sheehan syndrome)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.