Presentation
Chronic pain in the right 4th MCP. PH of acute episodes of great toe arthritis treated with indomethacin. Elevated serum urate.
Patient Data
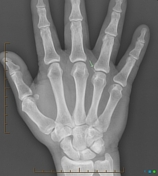
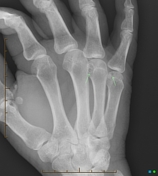
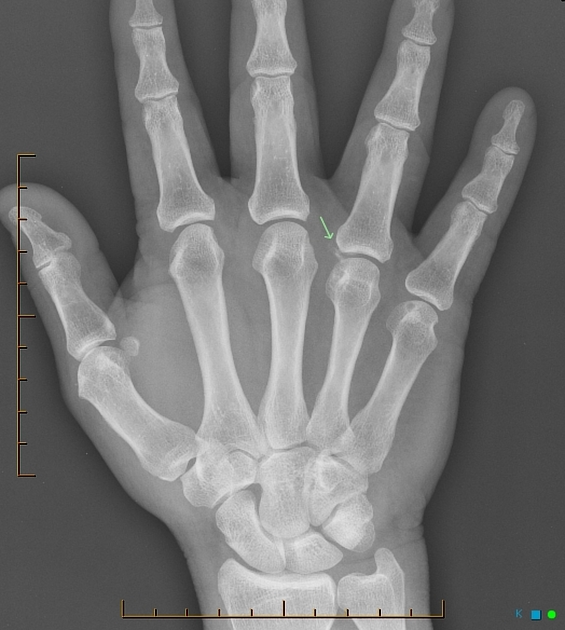
Subtle soft tissue hyperdenity (arrow) associated with a well-defined marginal erosion in the 4th metacarpal head and small lesion in the 5th (arrows).

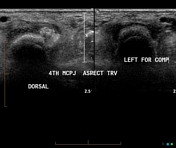
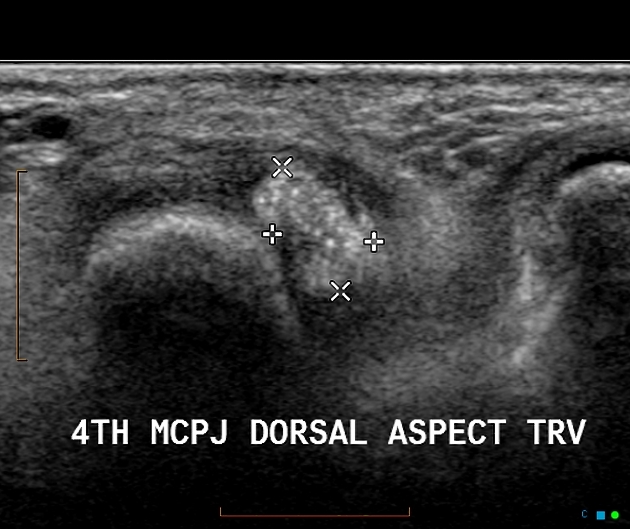
US performed to better define the location of soft tissue "calcification" seen on the radiograph
Echogenic mass in the 4th MCP corresponding to the x-ray finding. This is a deposit of uric acid (tophus). No abnormal blood flow to indicate an acute inflammatory process.
Case Discussion
People who have repeated attacks of gout or persistent hyperuricemia for many years can develop tophaceous gout. This designation describes the accumulation of large numbers of urate crystals in masses called tophi. These tophi develop in joints, bursae, bones, and cartilage, or under the skin. Tophi may cause erosion of the bone (marginal erosions) and eventually joint damage and deformity.
The presence of tophi near the knuckles or small joints of the fingers can be a distressing cosmetic problem. Tophi are usually not painful or tender but they can become acutely inflammed.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.