Presentation
Violently assaulted to the face. There was significant left orbital swelling. A CT trauma series was performed.
Patient Data


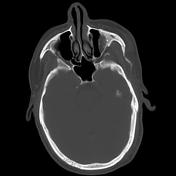


Left orbital floor fracture demonstrated, with herniation of the orbital contents into the maxillary sinus, including the inferior rectus muscle.
Case Discussion
Orbital fractures are common, occurring in 10-25% of all cases of facial fracture 1. Common mechanisms include blunt trauma, mainly from assault and motor vehicle accident.
The inferior orbital wall is most commonly affected by fracture 2. Signs of orbital fracture typically include peri-orbital bruising and subconjunctival hemorrhage. Furthermore, due to entrapment of the inferior rectus muscle, there may be restriction of downgaze in the affected eye.
Thin-sliced CT is the modality of choice in assessing orbital fracture 3. Cuts should be between 2-3 mm in thickness.
Management for orbital fractures is controversial 3. Guidelines for surgical management include:
persistent diplopia after settling of initial trauma
enophthalmos greater than 2mm after 14 days
large orbital floor fracture (greater than half) and/or associated with a medial wall fracture
Case contributed by A/Prof. Pramit Phal.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.