Presentation
Painless lump in right breast. The mass was palpable and mobile, of about 1 cm, located near the inframammary fold of the lower-inner quadrant of the right breast.
Patient Data
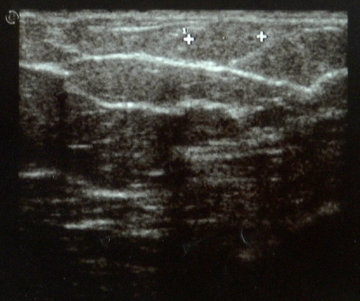
Breast ultrasound hardly shows an ovoid isoechoic mass with parallel orientation and without posterior acoustic shadowing.
The lesion was superficially situated and was hardly visible by breast ultrasound because it was isoechoic to the surrounding subcutaneous fat.

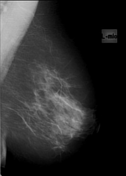
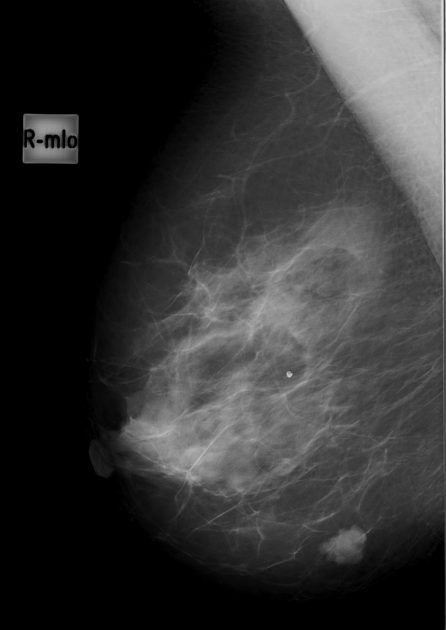
Mediolateral oblique mammogram shows a 1 cm dense mass with lobular shape and circumscribed margins, located superficially.
Case Discussion
A fine needle cytology was performed and no malignant cells were detected.
As the lesion had increased in size compared to a previous mammogram 2 years earlier, it was completely excised under local anesthesia. The final histological diagnosis was hemangioma, cavernous type.
Breast hemangiomas are rare benign vascular tumors in the breast with incidence between 1.2% (if clinically detested) and 11% (in post-mortem specimens). They generally are located superficially in the subcutaneous tissue and as such are palpable. Cavernous hemangiomas are the most common type. Their progression to malignant change is controversial.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.