Presentation
Four weeks of headache.
Patient Data
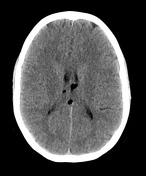

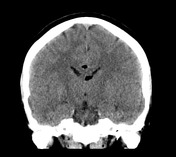

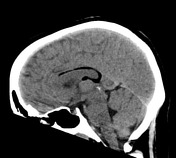


There is a thin fat density structure that lies superior to the corpus callosum, and extends from the anterior aspect of the body of the corpus callosum posteriorly, wrapping around the splenium of the corpus callosum, and then passing anteriorly into the cistern of the velum interpositum. No obvious corpus callosum dysgenesis identified on CT. There are also two small fat density components within the bodies of the lateral ventricles bilaterally, larger on the left.
Conclusion:
No acute intracranial hemorrhage.
Incidental pericallosal lipoma (curvilinear subtype) with extension into the lateral ventricles.
Case Discussion
Intracranial lipomas are congenital lesions, most commonly found in a pericallosal distribution. Pericallosal lipomas are divided into tubulonodular and curvilinear subtypes, and can be associated with corpus callosum dysgenesis. Extension into the choroid plexus and lateral ventricles can occur. Other sites for intracranial lipomas include the quadrigeminal plate cistern, suprasellar cistern and cerebellopontine angle.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.