Presentation
Patient post total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oopherectomy with adjuvant radiotherapy. Also, distal left ureteral resection and ureteral implantation. Follow up cystogram.
Patient Data
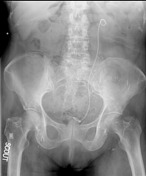
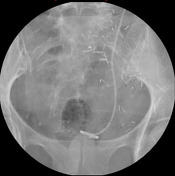

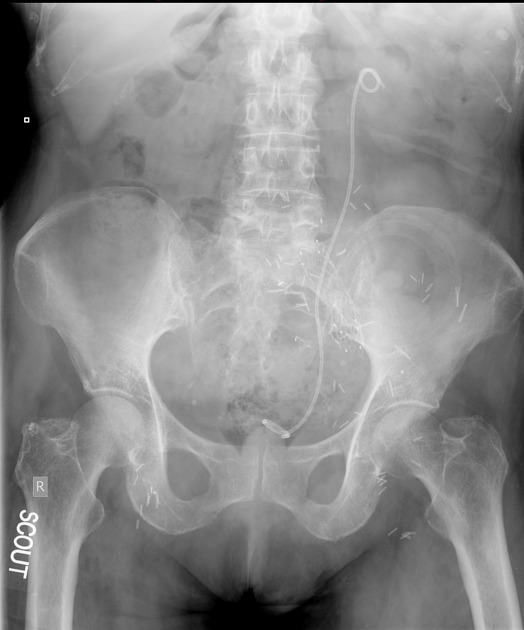
Scout radiograph: Numerous clips in the pelvis from TAH/BSO for a malignant uterine tumor. Left double-J ureteral stent. There is also a left iliac artery stent and a left lower quadrant colostomy. On the second coned-in scout radiograph, a round opacity at the level of the symphysis pubis represents a Foley balloon.
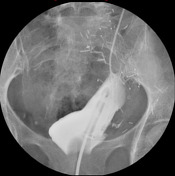
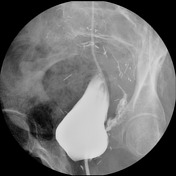
Cystogram: Contrast is introduced through a Foley catheter in the bladder. The bladder is deformed because of a psoas hitch. On progressive images, there is a wisp of contrast extending from the bladder into the left pelvis, compatible with a bladder leak. No vesicoureteral reflux.
Case Discussion
Bladder leak is risk of bladder and ureteral reconstruction, and it is not uncommon to acquire serial cystograms to monitor the progression of healing of a bladder or distal ureteral injury.
A psoas hitch is a method of adapting to a long distal ureteral injury. In a psoas hitch, the bladder dome is pulled toward the damage ureter to try to physically close the gap between bladder and undamaged ureter. A ureteral re-implantation on the bladder wall is then performed.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.