Presentation
New onset seizures.
Patient Data


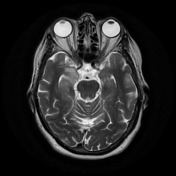



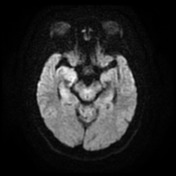

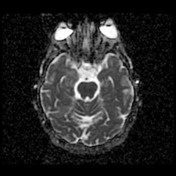

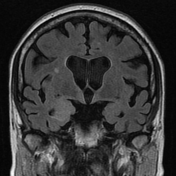

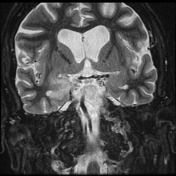

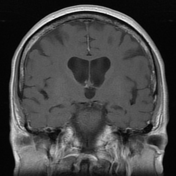

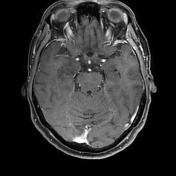

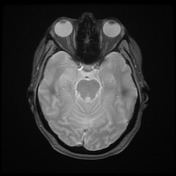


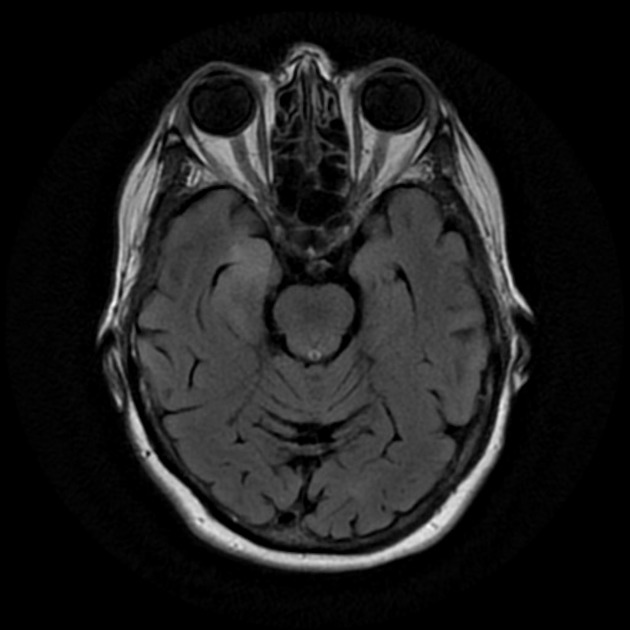
The hippocampal head, hippocampal body and amygdala on the right demonstrate increased T2 signal and appear bulkier than the counterpart on the left. There is increased DWI signal, with only slightly facilitated diffusion on ADC. There is apparent faint enhancement within the amygdala only seen on coronal images which is not definitely a real finding.
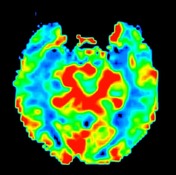
MR perfusion appears symmetric. MR spectroscopy is non-contributory.
Conclusion
Swelling increased T2 signal of the right hippocampus and amygdala has a differential of infiltrating tumor and limbic encephalitis (e.g. paraneoplastic). Limited, if any, change over the previous two weeks both on imaging and clinical status, makes herpes encephalitis very unlikely. The changes are too pronounced and persistent to represent post-seizure effects.
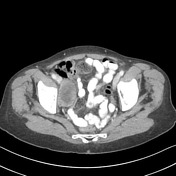

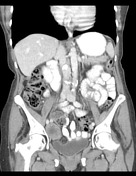

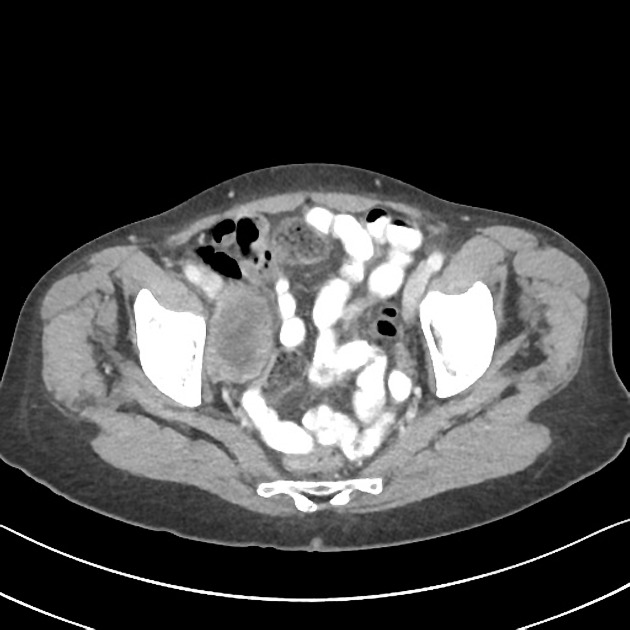
Heterogenous enhancing right adnexal mass is present.
A hypodense 1 cm lesion at the dome of segment 7 of the liver is incompletely characterized but possibly represents a hepatic cyst. No other focal liver lesion.
The spleen, adrenals, kidneys, pancreas, gallbladder, urinary bladder, uterus and left ovary are within normal limits.
No lymphadenopathy or free fluid.
Case Discussion
In this case, the imaging appearances and presence of a pelvic mass are compelling for the diagnosis of paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis.
CSF
The smear contains scattered lymphocytes, few monocytes and degenerate cells. No malignant cells are identified.
Lymphocytes 35
Monocytes 8
Neutrophils 0
Eosinophils 0
Antibodies and tumor markers
CA-125-New 16 U/mL (normal <35)
CA19.9-New 10 U/ml (normal <37)
Serum/Plasma CEA-New 2.7 ug/L (normal <5.0)
ISLET CELL ANTIBODIES - Serum/Plasma GAD (EIA) <0.6 U/mL (normal <5)
GABA-B Receptor Antibodies: NOT DETECTED
AMPA Receptor Antibodies: NOT DETECTED
NMDA Receptor Antibodies: Not Detected
Anti VGKC Antibody 9 pmol/L (normal <85 )
Anti-Hu (ANNA-1) antibodies POSITIVE.
Anti-Hu antibodies are detected in paraneoplastic peripheral neuropathy or encephalomyelitis, usually in the setting of small cell lung carcinoma, although many other primaries have been described including the ovary 1.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.