Presentation
Left loin pain.
Patient Data


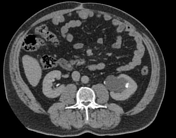

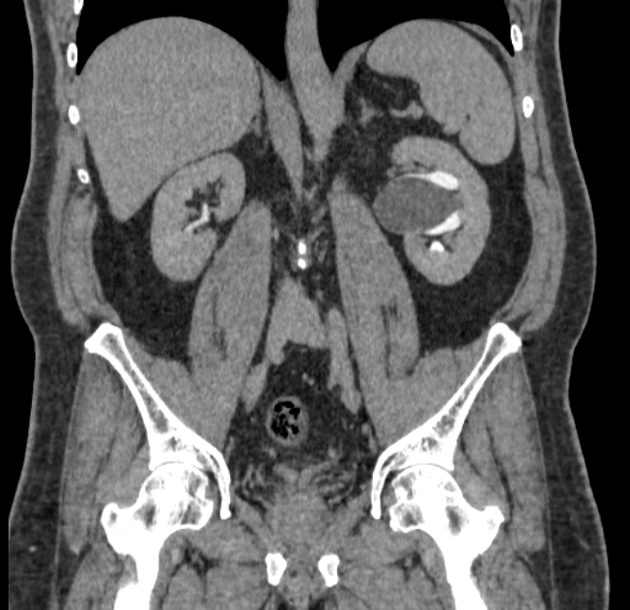
The left kidney showed renal sinus cyst stretching and displacing pelvicalyceal system which is minimally dilated as compared to the right kidney.
Case Discussion
A parapelvic cyst at times may cause compression of the pelvicalyceal system resulting in hydronephrosis. Parapelvic cyst can mimic hydronephrosis and so can be confused with pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction as the ureter in both conditions is not dilated. This could be well differentiated at the excretory phase of CT-IVP study (CT urography) that demonstrates stretched (but not dilated) collecting system by the cyst in contrary to PUJ obstruction at which the contrast will be excreted inside the dilated pelvicalyceal system. It can cause pelvicalyceal system dilatation by its mass effect.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.