Presentation
Recurrent shoulder dislocation
Patient Data
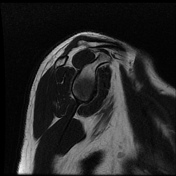

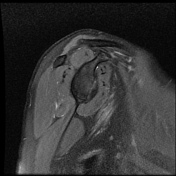

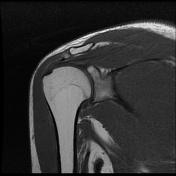

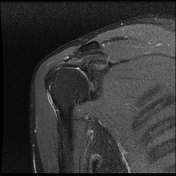

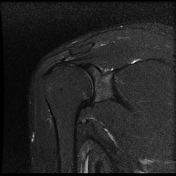

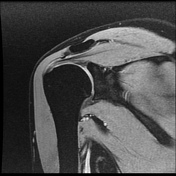

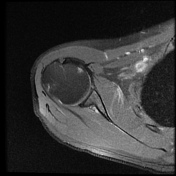

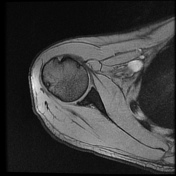

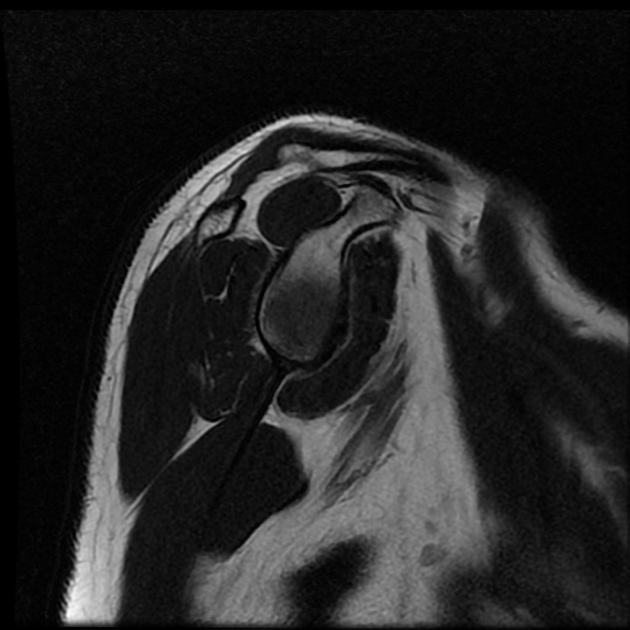
Intermediate signal intensity seen in all pulse sequences in the supraspinatus tendon. PD high signal intensity seen in anteroinferior labrum from 3 to 6 o clock.
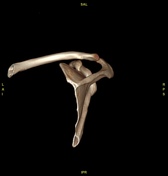

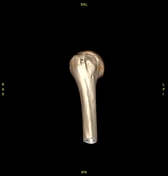

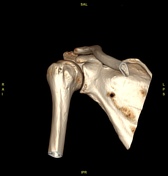

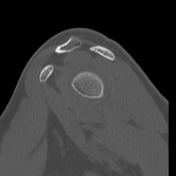

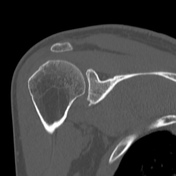

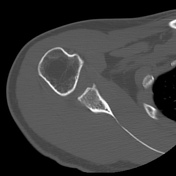

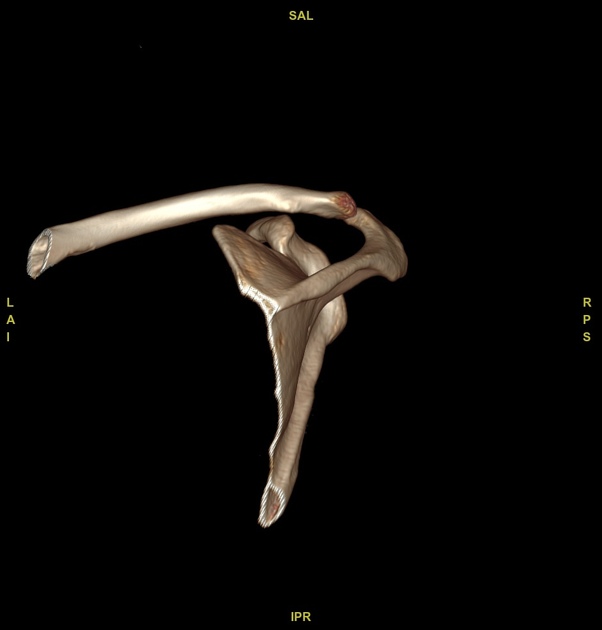
Bony depressed 7 mm fracture seen in the anteroinferior glenoid margin. Osteodegenerative changes seen in the posterosuperolateral humeral head.
Case Discussion
Recurrent anterior dislocation with a torn anteroinferior labrum and associated glenoid bony fracture is a typical case of bony Bankart. There is associated Hill Sach lesion in the posterosuperolateral humeral head. <5% glenoid volume loss in this case.
This is a typical example of bony Bankart with Hill Sach lesion.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.