Presentation
Generalized pains in knees/bones. Family history of a 'bone condition' causing pain and deformity. Markedly elevated serum alkaline phosphatase.
Patient Data

Lateral film only.
There are mixed sclerotic and lucent lesions throughout the skull, with coarsened trabeculae in the calvarium, in keeping with Paget disease of bone.
Some sclerosis is also noted in the superior endplate of C4, which could equally be degenerative in nature.
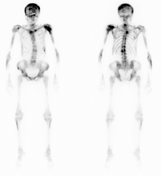


NM injection: tracer injection in left antecubital fossa.
NM bone whole body :
There is intense tracer uptake in the skull, upper thoracic and upper lumbar spine, medial left clavicle, left lower rib cage and left humeral head: glenoid; and relatively mild diffuse increased tracer uptake in the remaining skeleton. Intense bone activity results in a lack of excreted activity in the kidneys and bladder.
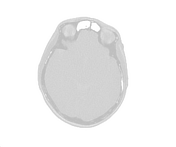
SPECT-CT skull shows heterogeneous intense tracer uptake in the skull associated with mixed sclerosis and lucent areas, and patchy ground glass changes.
SPECT-CT thoracic and lumbar spine shows widespread mixed sclerotic and lucent areas and increase trabeculation in the spine, scapulae, humeri, clavicles, sternum and pelvic bones. Intense bone tracer activity as in the above whole body scan.
Marked scoliosis noted.
Conclusions:
Very unusual case. Although the age and sex demographics are unusual, the radiological findings are more in keeping with Paget disease with polyostotic fibrous dysplasias less likely.
Case Discussion
Subsequent bone scan confirmed Paget disease as the most likely pathology here. Differential diagnosis includes polyostotic fibrous dysplasia.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.