Presentation
Uncertain cause for initial imaging.
Patient Data

On the left, the posterior part of the vestibular aqueduct and adjacent bone are eroded.
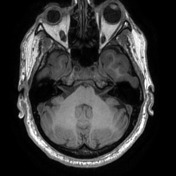



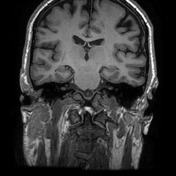

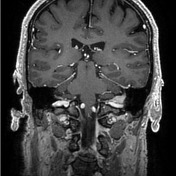

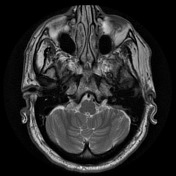

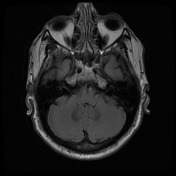

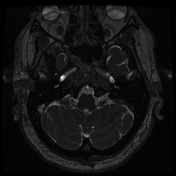

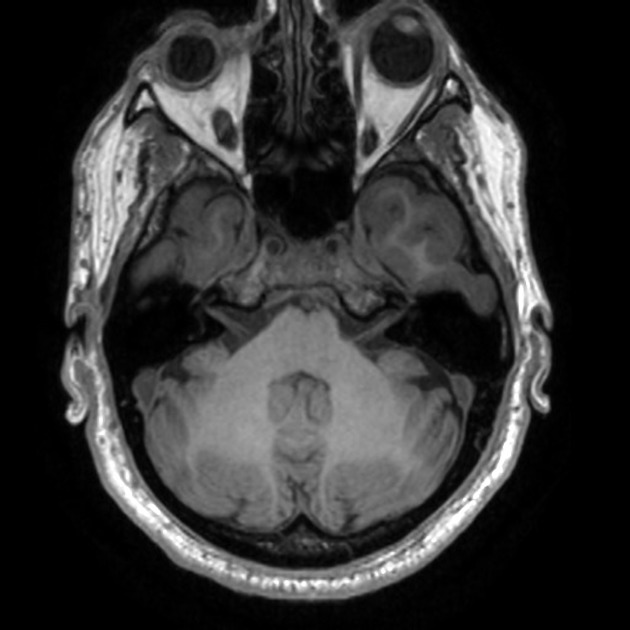
Best seen on axial T1 with contrast is an extra-axial mass located at the expected location of the left endolymphatic sac (posterior aspect of the petrous bone). It is lobulated and vividly enhancing with erosion of the adjacent bone. Inferiorly it involves but does not occlude the sigmoid sinus.
Conclusion: given the location and erosion of bone an endolymphatic sac tumor is favored.
Case Discussion
The patient went on to have resection.
Histology
The sections show a moderately cellular tumor. It forms elongated nests and acinar-like structures. Some contain calcific deposits and psammoma bodies. The tumor cells have round nuclei, inconspicuous nucleoli and moderate amounts of 'oncocytic type' eosinophilic cytoplasm.
The tumor cells are CAM5.2, AE1/3, CK7, EMA, S-100 and SOX-10 positive. Progesterone receptor, melan-A, synaptophysin, TTF-1 and thyroglobulin are negative.
The PAS stain shows no fungi. The Ziehl-Neelsen stain shows no acid-fast bacilli. Though the architecture is not quite papillary but given the immunoprofile and the site, the features are consistent with papillary tumor of the endolymphatic sac.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS: Papillary tumor of the endolymphatic sac.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.