Presentation
Imbalance while walking, abnormal movements and dementia.
Patient Data


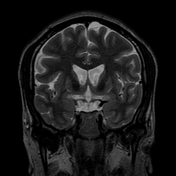

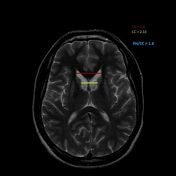
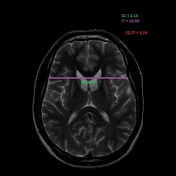
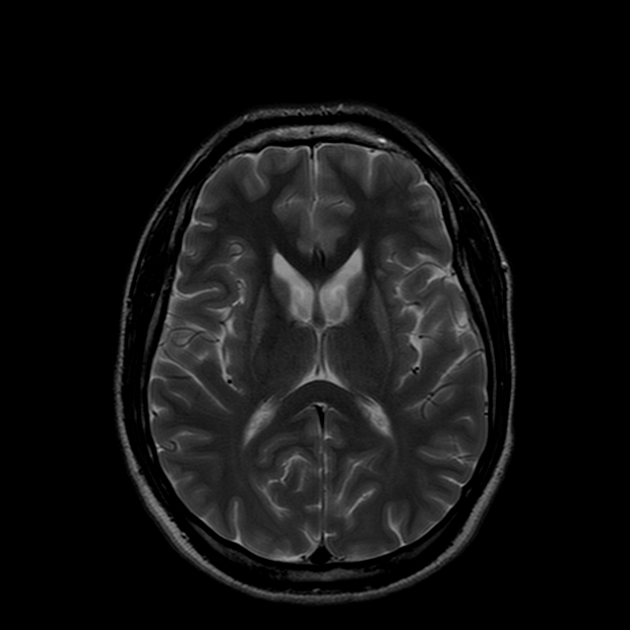
Atrophy of the caudate nucleus and putamen with concomitant enlargement of the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles.
The inter caudate distance is 2.13, the frontal horn width is 3.4,and the inner table width is 10.96. Thus, the frontal horn width to intercaudate ratio (FH:CC) is low 1.6 (normal = 2.2-2.6) and the intercaudate distance to inner table ratio (CC:IT) is increased 0.19 (normal = 0.09-0.12)
All the above calculations and the clinical history are consistent with Huntington disease.
Case Discussion
Huntington disease (Huntington chorea), is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease in which there is trinucleotide (CAG) repeat. It is caused by a loss of GABAergic neurons of the basal ganglia, especially in the caudate nucleus and putamen, resulting in atrophy of those structures.
Clinically, patients present with progressive involuntary choreoathetoid movements, dementia, and psychosis which starts in midlife.
On imaging, patients characteristically have atrophy of the caudate head, which can be quantified by two ratios:
- frontal horn width to intercaudate distance ratio (FH/CC) is decreased
- intercaudate distance to inner table width ratio (CC/IT) is increased
This particular patient had classic clinical and imaging features, and on genetic study, trinucleotide repeats were present, which confirmed the diagnosis of Huntington disease.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.