Presentation
Wrist pain.
Patient Data
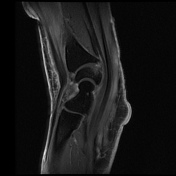

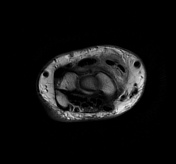



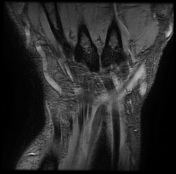



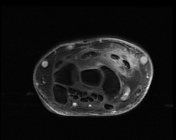

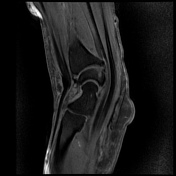

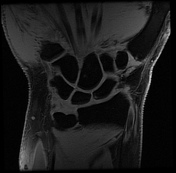


There is soft tissue edema around the area of the crossing of extensor pollicis longus (EPL) over the second extensor compartment (extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) and extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL). There is fluid signal intensity within the synovial sheath of ECRB, the second and third extensor tendon compartments in keeping with tenosynovitis with a mild interstitial tear of the ECRL and EPL tendons.
Cystic changes of the carpal bones. Unremarkable flexor tendons. Normal appearance of the median nerve. Normal appearance and signal intensity of the triangular fibrocartilage. No joint effusion present.
The overall imaging feature is compatible with distal intersection syndrome.
Case Discussion
Intersection syndrome is a result of repetitive stress or trauma resulting in tenosynovitis and peritendinous edema in the extensor tendons compartments, two types have been described, the proximal type and the distal type. This case shows the typical features of distal intersection syndrome where the third extensor compartment tendon (the extensor pollicis longus) crosses over the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis tendons.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.