Presentation
bilateral parotid enlargement treated as chronic parotitis.
Patient Data
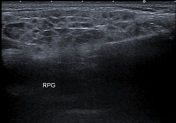
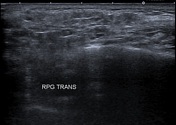
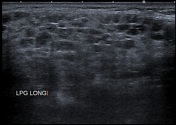
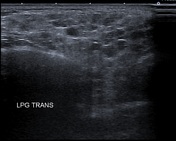
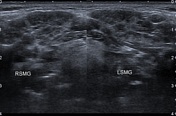
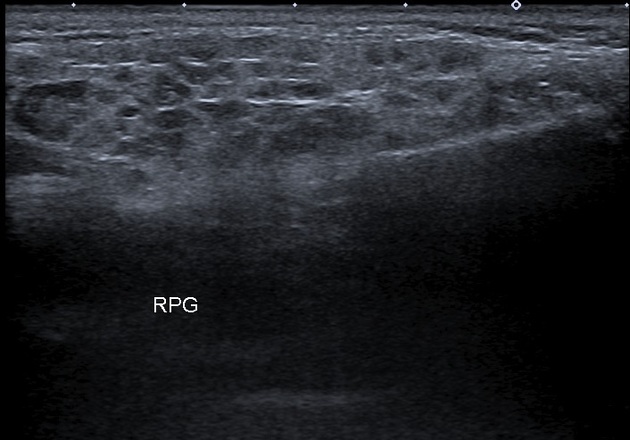
Both parotid and submandibular glands appear relatively enlarged with multicystic changes and reticular pattern.
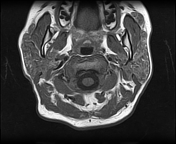

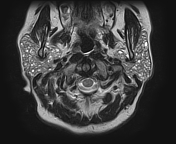

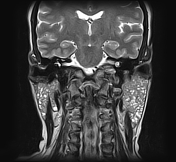

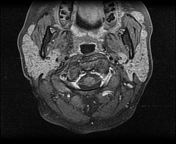

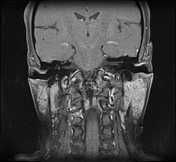


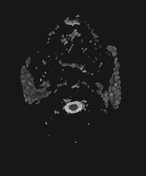


Both parotid glands are enlarged with innumerable cystic lesions disseminated in both parotid glands, of low signal onT1, hight signal on T2, giving a honeycomb appearance. On moderate heterogeneous enhancement is noted on postcontrast sequences.
Both submandibular glands show a similar but much less prominent involvement as compared to the parotid glands.
Case Discussion
Ultrasound and MRI features are characteristic of Sjögren syndrome.
Follow-up is mandatory in such case due to the high risk of developing a malignant lymphoma




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.