Presentation
Osteopenic and low calcium levels.
Patient Data
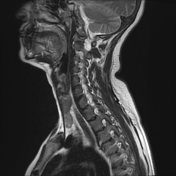



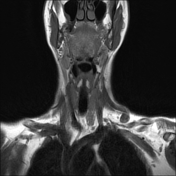

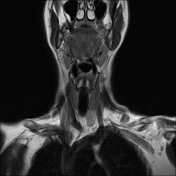

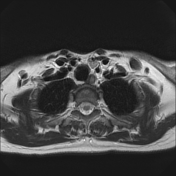

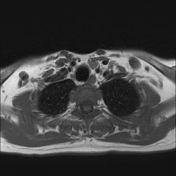

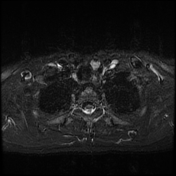

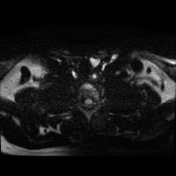

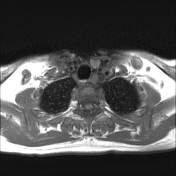

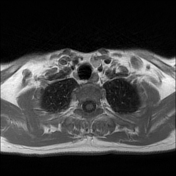

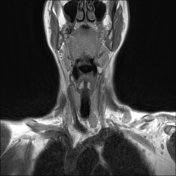

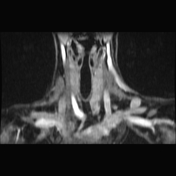

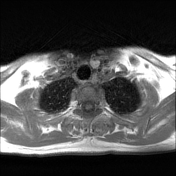

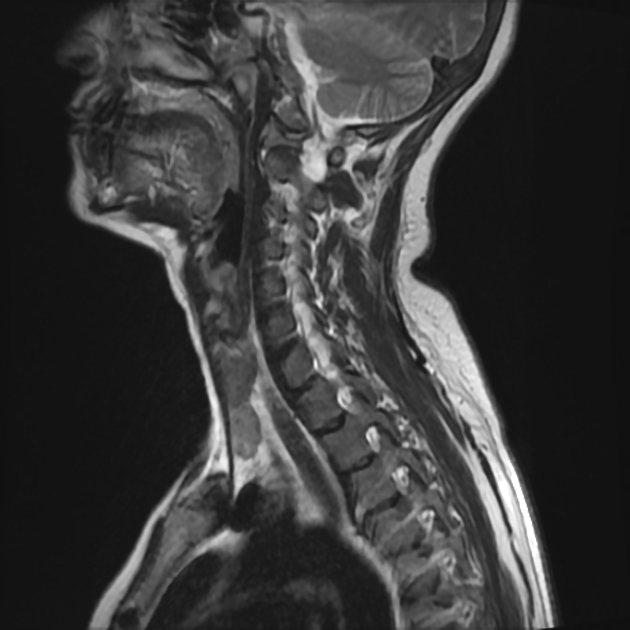
Left lower deep cervical well defined soft tissue mass lesion is seen attached to the inferior pole of the left thyroid lobe. It measures 1.4x1.2 x 2.5 cm along its max TS, AP & CC dimensions. It elicits low signal at T1 high T2 signal at T2 & STIR WI with mild diffusion restriction and post contrast enhancement.
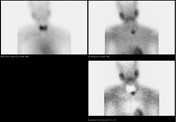
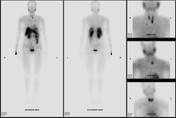
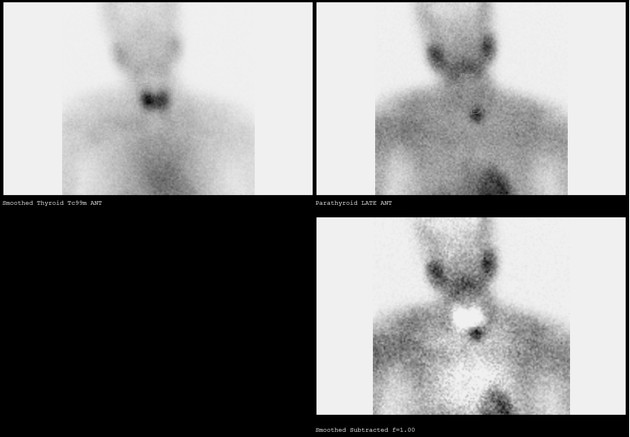
Immediately caudal to the left thyroid lobe, there is punctate uptake in the early phase (15 min registration) that remains active during the late phase (2 hours). The localization of this uptake matches the lesion identified on MRI confirming parathyroid adenoma.
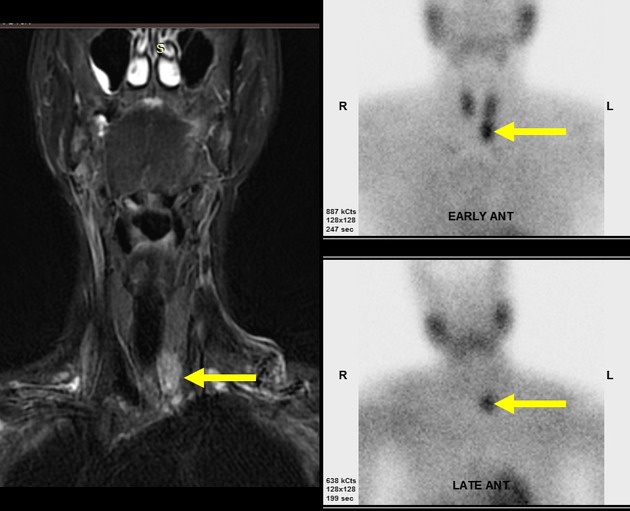
Well defined soft tissue mass lesion is abutting the inferior pole of the left thyroid lobe. It shows punctate uptake in the early phase (15 min registration) that remains active during the late phase (2 hours) characteristic of parathyroid adenoma.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.