Presentation
Sudden headaches with left ophthalmoplegia in a patient with a pituitary mass.
Patient Data


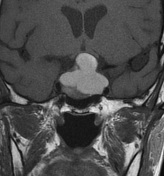

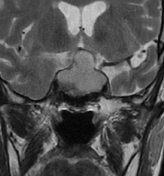

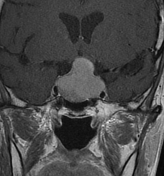

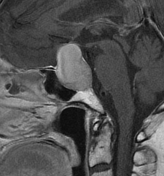

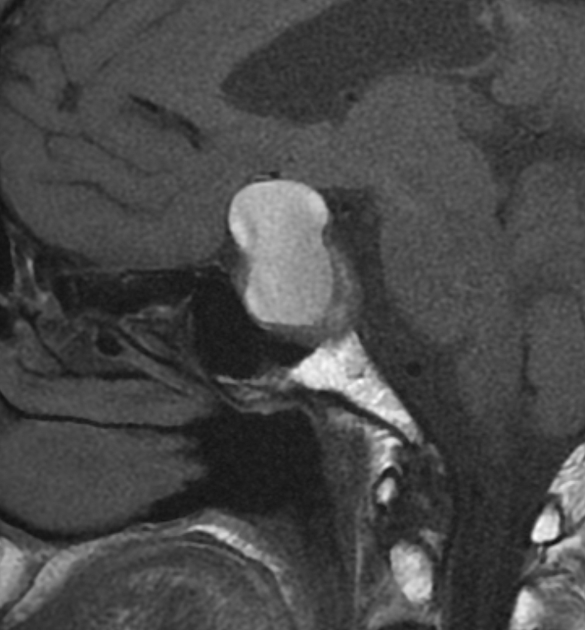
There is a sellar mass with suprasellar extension elevating the optic chiasma. It shows a large central area of high signal on T1WI/T2WI with no enhancement on postcontrast sequences in keeping with a central hemorrhagic infarction. The non-necrotic component is of right posteroinferior location of intermediate signal on T1WI/T2WI with moderate and relatively homogeneous enhancement.
Case Discussion
The clinical presentation and the MRI features in a patient with a pre-existing pituitary macroadenoma are most consistent with pituitary apoplexy.
Pituitary apoplexy is an acute clinical syndrome caused by either hemorrhage or infarction of the pituitary gland. Although variable, it typically comprises of a headache, visual deficits, ophthalmoplegia, and altered mental status. An existing pituitary macroadenoma is usually present (60-90%) but it can occur with healthy glands in a few isolated cases.
Additional contributor: ZE. Boudiaf, MD




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.