Presentation
Headache and convulsions.
Patient Data
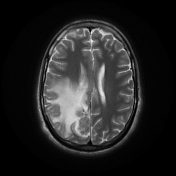

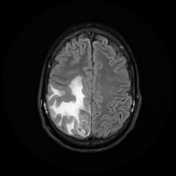

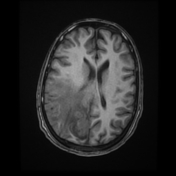

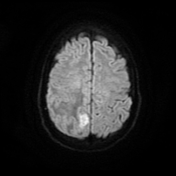

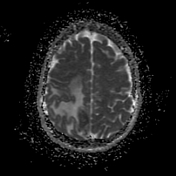

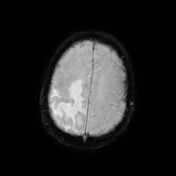

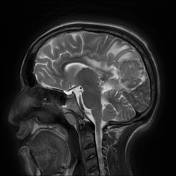

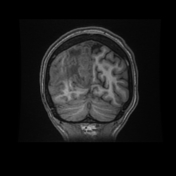

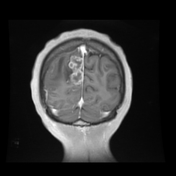



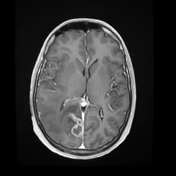

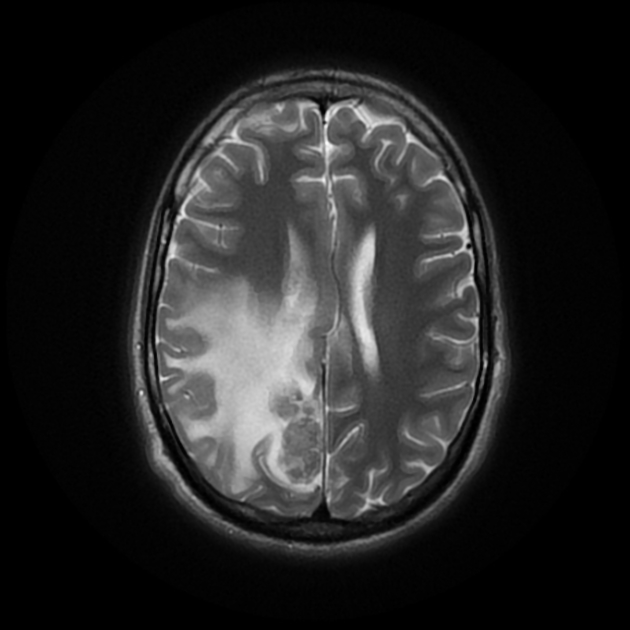
Right parietal parafalcine cortical/gyral space occupying lesions of abnormal signal. They elicit isointense signal at T1 WI, low signal at T2 WI with diffusion restriction and marginal nodular post contrast enhancement. The lesions are surrounded by subcortical vasogenic edema signal which exert positive mass effect in the form of ipsilateral right lateral ventricle and effacement of the overlying cortical sulci.
The patient tested positive for sputum acid-fast bacillus (AFB) and Genexpert for tuberculosis.
CSF analysis revealed high protein, low glucose and positive for AFB.
A CT scan of the chest was performed to detect pulmonary tuberculosis.
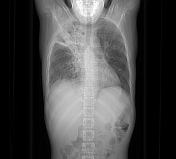
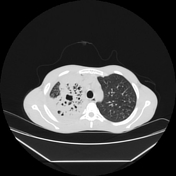

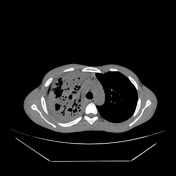

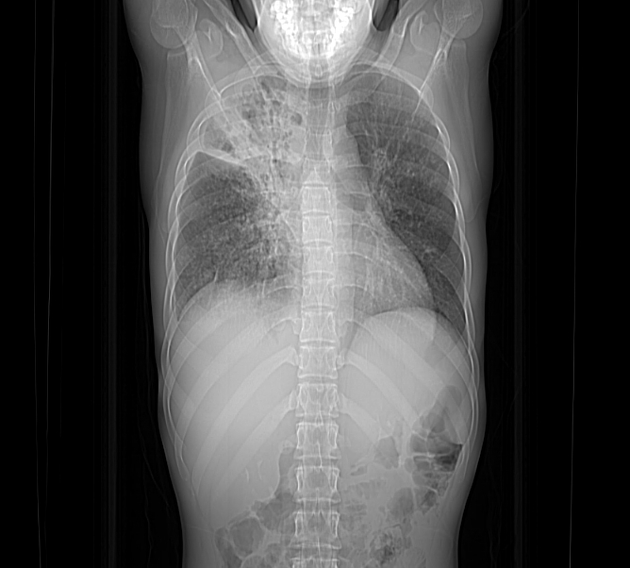
Right upper lobar air-space consolidations showing multiple cavitary lesions. Right lower lobar multiple small consildative patches. Bilateral pulmonary tree-in-bud densities. Mild right pleural effusion.
Case Discussion
The characteristic low signal of the lesions on T2 WI and the ring enhancement raised suspicion of granulomatous disease, mostly tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis of the central nervous system can result from either hematogenous spread from distant systemic infection (e.g. pulmonary tuberculosis), as in our case.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.