Presentation
Dizziness, headache, and left side weakness.
Patient Data
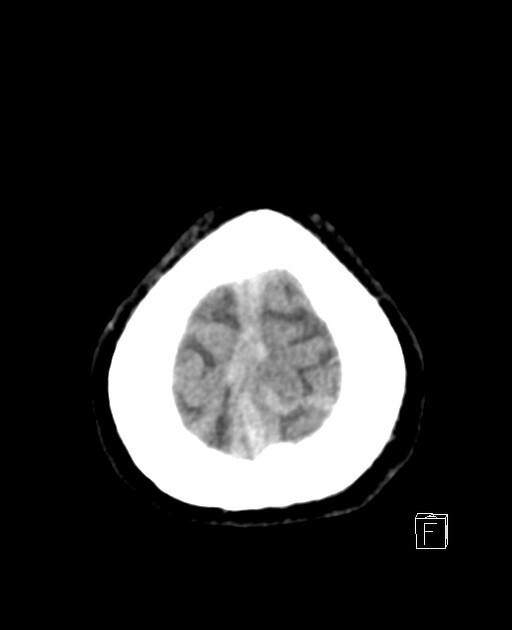
Increased density of the superior sagittal sinus and left upper cortical vein for better assessment by MRI and MRV to rule out thrombosis.
Normal brain, brain stem, and cerebellar density.
No acute intracranial hemorrhage or obvious acute infracts.

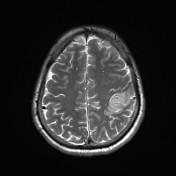




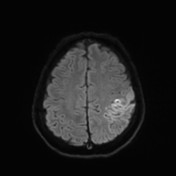

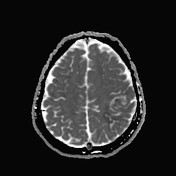



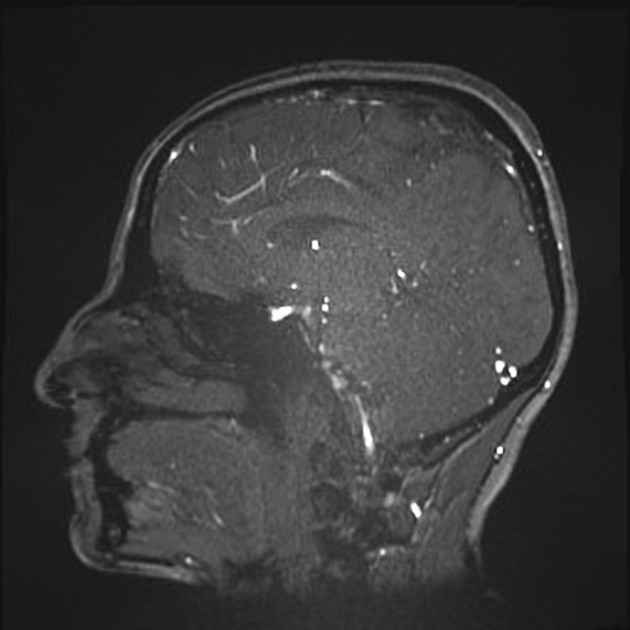
Abnormal signal of the superior sagittal sinus and upper frontoparietal cortical veins, more in the left side indicating dural sinus and superficial veins thrombosis for better assessment by MRV.
Suspicion of an abnormal signal is also seen in the left transverse sinus.
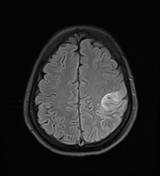
An abnormal signal is seen in the left upper parietal cortex with diffusion restriction, indicating acute ischemia for follow-up with CT or MRI scan to rule out associated parenchymal hemorrhage. A similar faint signal is also seen in the left temporal cortex.
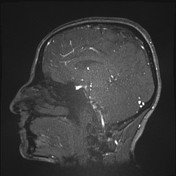

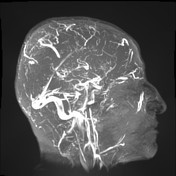

The superior sagittal sinus is not visualized indicating extensive thrombosis, and filling defects are seen in the left transverse sinus suggestive also of thrombosis.
The inferior sagittal sinus, internal cerebral veins, and the straight sinus are visualized.
Case Discussion
This is a 40-year-old lady presenting through ER with dizziness, headache, and left side weakness. CT scan was requested and showed dense superior sagittal sinus and congested left upper cortical vein, MRI and MRV were advised for further evaluation of suspected venous thrombosis. It showed an abnormal signal in the frontoparietal veins more on the left, thrombosis in the superior sagittal and left transverse sinuses. An associated abnormal signal in the brain parenchyma indicating associated infarction causing diffusion restriction at the left parietal and temporal cortices.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.