Presentation
Wrist pain and swelling. History of hand trauma a year ago.
Patient Data
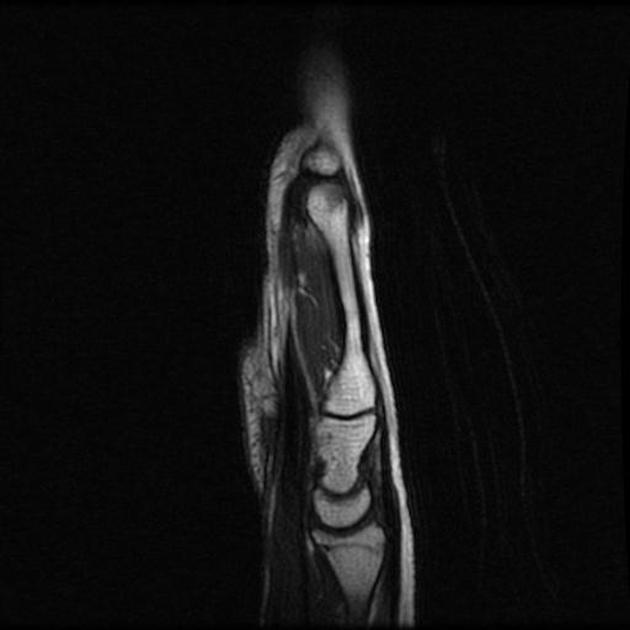


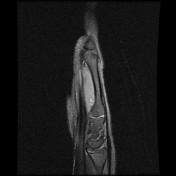

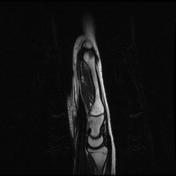

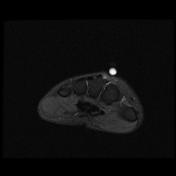

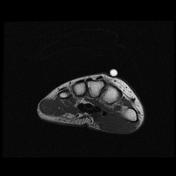

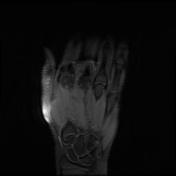

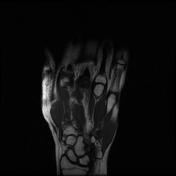


Abnormal intrasubstance increased signal and surrounding edema is seen along the course of extensor pollicis longus (EPL) when crossing the extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) and extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) tendons associated with ECRL and ECRB tenosynovitis.
Bony protuberance at the site of swelling pointed by the patient is prominent osteophytes at the base of the third metacarpal and its articulation with the capitate bone representing carpal boss.
Case Discussion
The ECRB, ECRL, and EPL tendons intersect distal to Lister’s tubercle and radiocarpal joint. The tubercle acts as a pulley, changing the EPL tendon angle when it crosses superficially over the ECRL and ECRB tendons. This creates a mechanically disadvantageous arrangement, where the motion of the thumb and hand may cause friction between these tendons.
The carpal boss is a hypertrophied bony protuberance on the dorsal surfaces of the base of the second or third metacarpals, near the capitate and trapezium. It may be bilateral.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.