Presentation
Sudden onset headache.
Patient Data
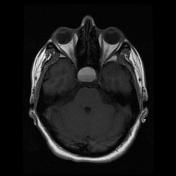



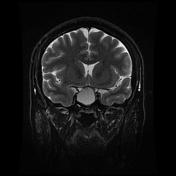

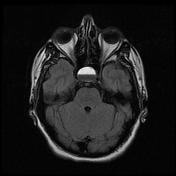

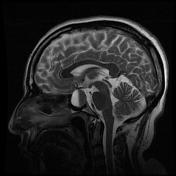


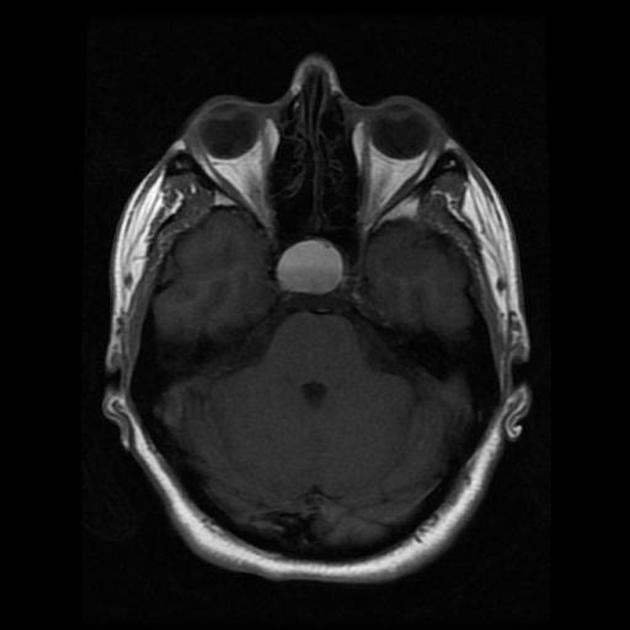
An expansile ovoid mass lesion measuring about 20 x 25 mm in the pituitary fossa with suprasellar extension displacing the optic chiasm superiorly.
The lesion has an intrinsic T1 signal consistent with hemorrhage, also with a hematocrit level within. No calcifications.
High signal foci on T2 and FLAIR sequences at subcortical and periventricular white matter of both cerebral hemispheres depict microvascular ischemic events.
Case Discussion
Pituitary apoplexy is an acute clinical syndrome caused by either hemorrhagic or non-hemorrhagic necrosis of the pituitary gland. Although variable, it typically comprises headache, visual deficits, ophthalmoplegia, and altered mental status. An existing pituitary macroadenoma is usually present (60-90%), but it has occurred with healthy glands in a few isolated cases.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.