Presentation
Long-stay polytraumatic patient with right upper neck swelling.
Patient Data
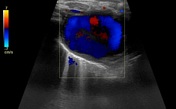
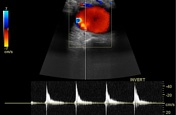
A right cervicothoracic vascular lesion shows internal turbulent flow with a characteristic "to and fro" pattern in the pulsed Doppler study.
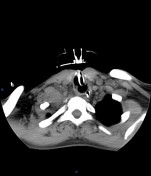

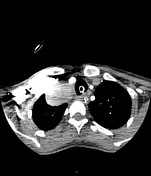

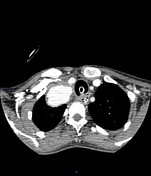

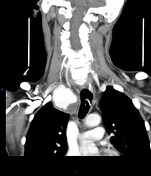

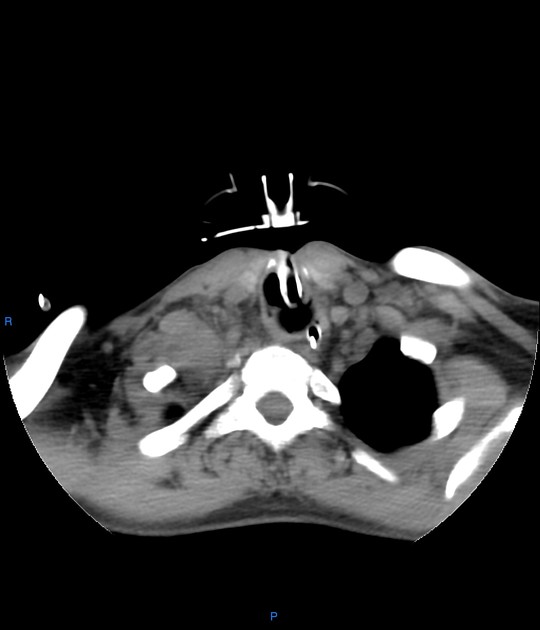
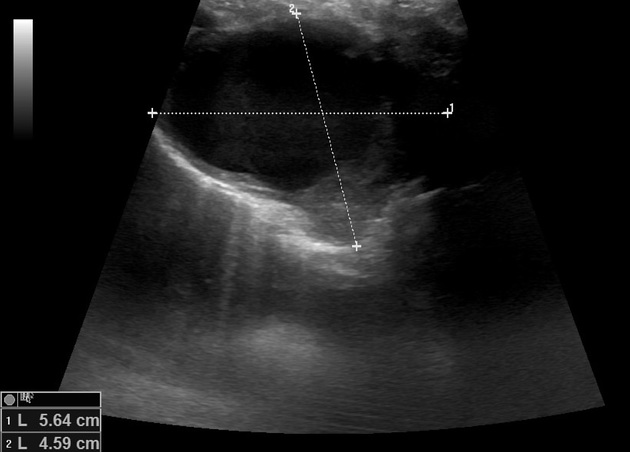
Right cervicothoracic large vascular lesion seen smoothly indenting the right lung apex and closely related to the vascular structures, it measures 4x4.5x6 cm and presents heterogeneous density on the non-enhanced study.
In the angiographic study, the lesion is almost completely enhanced in the late arterial phase with direct communication with the proximal right subclavian artery, the connection measures 5mm diameter and 10mm length.
Tracheostomy and nasogastric tubes are noted.
Case Discussion
Here is a case of subclavian artery pseudoaneurysm with typical imaging criteria. The patient was a long stay polytraumatic, and an iatrogenic injury was suspected to be the cause of pseudoaneurysm (arterial catheterization during a trial of central venous access). A plain CT study of the neck was done first for airway assessment and the lesion was discovered incidentally and a duplex study was recommended.
An important tip here is that if any detected mass-like lesion with unknown nature, the vascular possibility must be excluded first especially if the lesion is related to the vascular structures to avoid catastrophic bleeding with any intervention.
Ultrasound contribution by Dr. Somia Elbadawy




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.