Presentation
Headache.
Patient Data
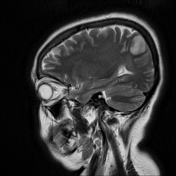

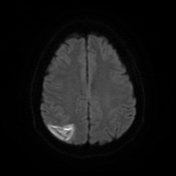

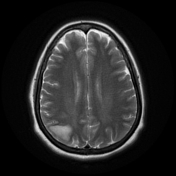

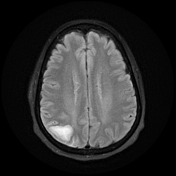

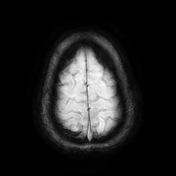

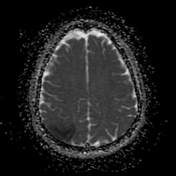

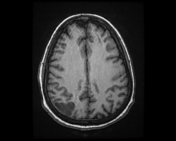

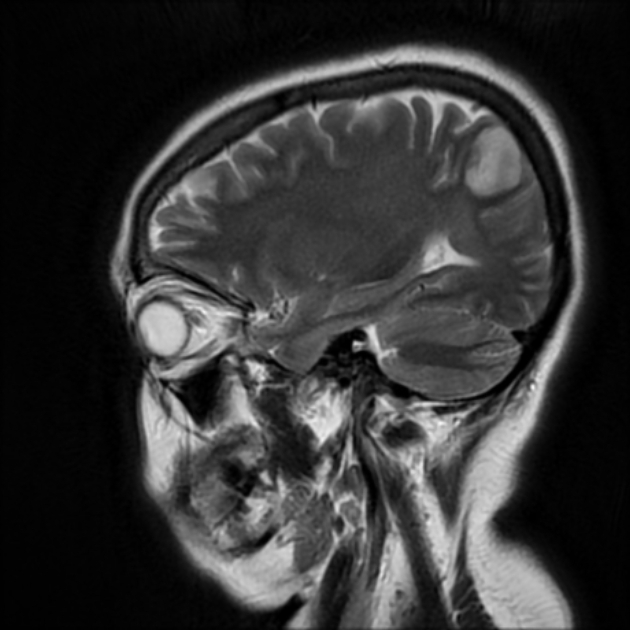
Right parietal cortical and subcortical area of abnormal signal and diffusion restriction with internal blooming on SWI, in keeping with hemorrhagic infarction, associated with adjacent subarachnoid hemorrhage. Adjacent right parietal prominent draining cortical vein showing loss of normal signal void and eliciting high signal on T2 & FLAIR WI with diffusion restriction and blooming on SWI.
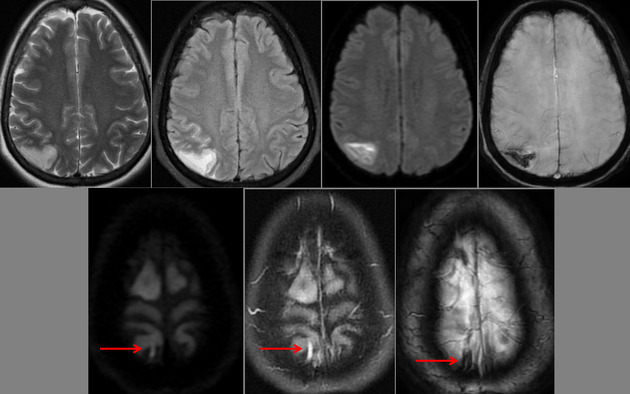
The photo illustrates the right parietal venous infarction and adjacent subarachnoid hemorrhage.
The draining venous cortical vein (Red arrows) appears prominent eliciting high signal on FLAIR WI, diffusion restriction and blooming on SWI.
Case Discussion
Isolated cortical vein thrombosis is rare and represents 1% of cerebral infarctions. It occurs with occlusion of one or more of the cerebral cortical veins without occlusion of the major dural venous sinuses.
The thrombosed cortical vein might be seen on a non-contrast CT/MR scan.
Parenchymal hemorrhagic venous infarction, parenchymal hematoma, parenchymal edema (venous congestion), or subarachnoid hemorrhage might be seen at the parenchymal areas drained by the thrombosed cortical vein.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.