Presentation
Acute right iliac fossa pain, leukocytosis.
Patient Data
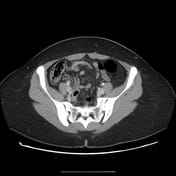

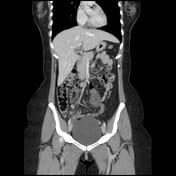

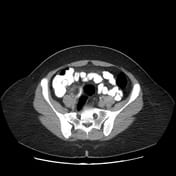

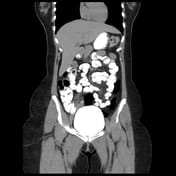

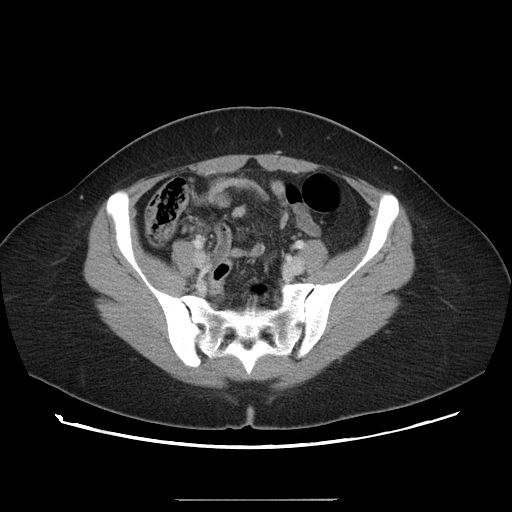
The appendix appears dilated measures 10 mm, and shows a thickened enhanced wall, edematous peri appendiceal fat, and multiple regional lymph nodes. There are no currently related masses or collections.
Most of the appendical lumen is obliterated apart from the short proximal segment showing a trace of enteric contrast.
A right ovarian cyst is noted.
Case Discussion
This is a classic presentation of acute appendicitis on CT, later confirmed by histopathology following laparoscopic appendectomy. The pathogenesis of acute appendicitis is typically attributed to luminal obstruction, which is usually complete.
However, this case demonstrates an atypical partial obstruction of the appendiceal lumen, evidenced by partial opacification with enteric contrast.
Despite this unusual feature, the diagnosis of acute appendicitis remained straightforward, supported by a typical clinical presentation, leukocytosis, and definitive inflammatory signs on CT.
This observation also sheds light on the pathogenesis of spontaneously resolving acute appendicitis, which occurs in approximately 38% of cases 1. Such resolution is thought to result from the spontaneous relief of luminal obstruction, leading to the subsidence of inflammatory changes.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.