Presentation
Work up for acute left-sided abdominopelvic pain.
Patient Data
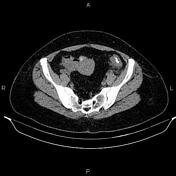

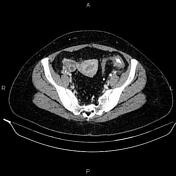

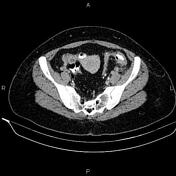

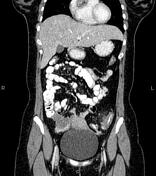

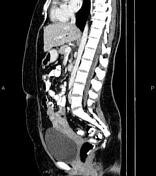


Multiple diverticula are seen at the left hemi-colon, accompanied by segmental increased wall thickness at the sigmoid colon with surrounding fat stranding most consistent with acute diverticulitis. There are no signs of perforation, secondary abscess formation, and fistula formation.
Case Discussion
On imaging, colonic diverticulitis is characterized by segmental colon wall thickening with surrounding fat stranding and adjacent diverticula, usually in the sigmoid. Pericolic fat stranding is often disproportionately prominent compared to the amount of bowel wall thickening.
Extravasation of gas and fluid into the pelvis and peritoneal cavity suggests diverticular perforation. Abscesses and fistula formation (usually a chronic complication) may be seen in complicated cases.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.