Presentation
Acute respiratory distress following diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.
Patient Data
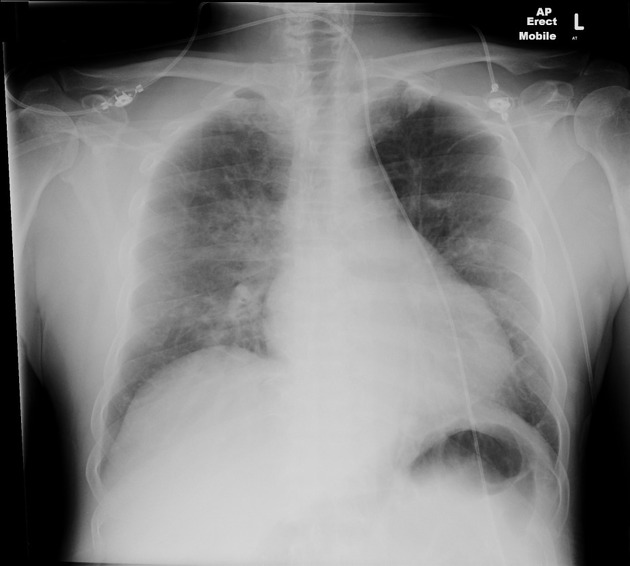
There is increased interstitial markings, upper lobe vascular redistribution and perihilar opacification in keeping with acute pulmonary edema. Appearances are asymmetrical due to rotation, confirmed on a subsequent CXR 4 hours later for review of CVL placement (not available). Heart size is within normal limits for AP projection.
Case Discussion
There is a long list of cardiogenic and non-cardiogenic APO, but further Hx from the patient and his wife is of a recent meal of tropical fish. There were no obvious causes for APO and the provision diagnosis was of ciguatera. Supportive treatment resulted in the patient improving over several days and he was discharged 3 days later symptom free and with a normal CXR.
Ciguatera is the acute toxicity syndrome caused by the naturally occurring ciguatoxin from the dinoflagellate microscopic algae Gambierdiscus toxicus. It is is found in tropical fish and is the most common cause of fish poisoning worldwide. Ciguatera is synthesized by certain bacteria after phagocytosis by the G. toxicus algae, which is found in dead coral and algae in shallow tropical and subtropical waters, and then eaten by small fish. The toxin is concentrated in the aquatic food chain, and humans consume the toxin in tropical fish meat. Ciguatoxin is not affected by cooking or freezing.
Ciguatoxin is a neurotoxin which increases neuronal membrane excitability due to its action on voltage-gated sodium channels. It also affects the gastrointestinal and cardiovascular systems. Most commonly patients present with gastrointestinal symptoms initially within 6 hours of ingestion.
Gastrointestinal symptoms include:
- abdominal pain
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
Neurologic symptoms include:
- paresthesia
- lingual
- circumoral
- extremities, which maybe painful
- allodynia
- paradoxical temperature reversal
- pain
- dental
- arthralgia
- myalgia
- metallic taste
- hallucinations
- confusion
- headache
- pruritus
- ataxia and vertigo
- weakness
- respiratory paralysis
- coma
Cardiovascular manifestations usually occur with gastrointestinal and neurological symptoms, and include:
- hypotension
- bradycardia
- pulmonary edema
- arrhythmias




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.