Adrenal vein sampling and adrenal nodular hyperplasia - Conn syndrome
Presentation
History of longstanding hypertension. Renin was found to be low. A CT was requested to look for a pheochromocytoma.
Patient Data
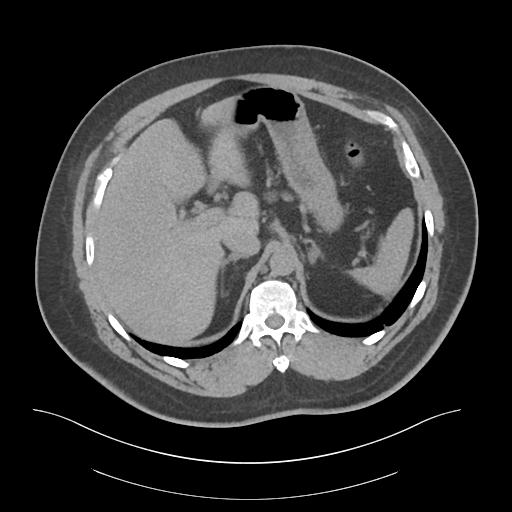
Nodular hyperplasia of the left adrenal gland (density 5-15 HU). The right adrenal gland appears normal.
Given the clinical history, this may represent an adrenal cortical adenoma causing Conn's syndrome. This may be further investigated with adrenal vein sampling and endocrinology aldosterone testing.
Adrenal vein sampling


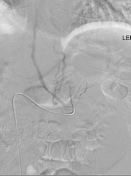

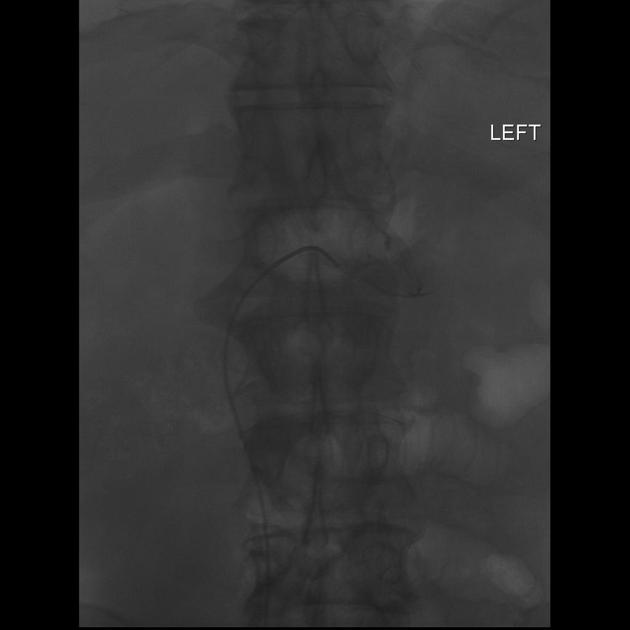
Specimens were sent for analysis of aldosterone and cortisone as requested.
Result: adrenal vein sampling
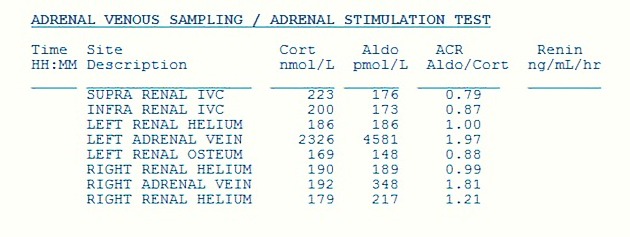
The sample from the left adrenal gland is clearly abnormal and in keeping with primary hyperaldosteronism.
Case Discussion
Primary hyperaldosteronism can be due to adrenal hyperplasia (60%), adrenal adenoma (40%), glucocorticoid-remediable hyperaldosteronism (dexamethasone-suppressible hyperaldosteronism), <1%, and rare entities, such as disorders of the renin-angiotensin system (<1%).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.