Presentation
Hyperextension injury while tackling.
Patient Data
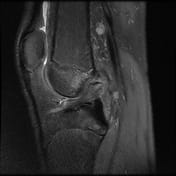

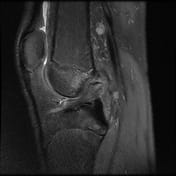

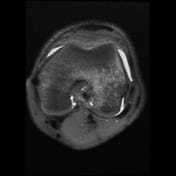

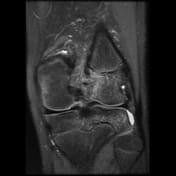

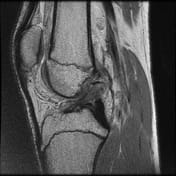

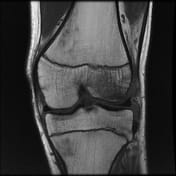

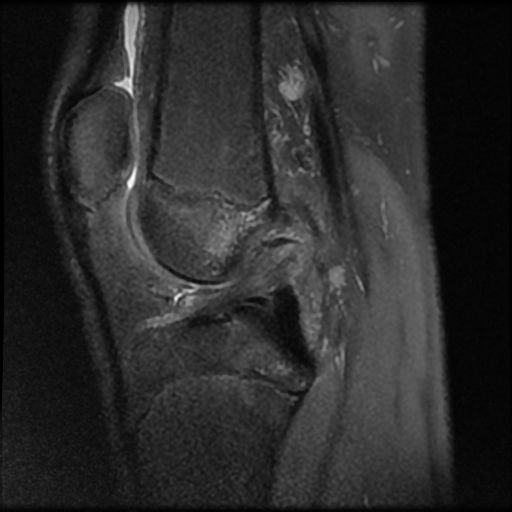
Pivot-shift contusion pattern with bone marrow edema involving the lateral femoral condyle, lateral tibia, and to a lesser extent the medial femoral condyle. Transverse linear low T1 signal line through the lateral femoral condyle subchondral bone in keeping with a subchondral fracture.
Mildly displaced osseous avulsion from the femoral attachment of the ACL with linear fragment within the posterosuperior intercondylar region. The more caudal ACL fibers have a redundant flattened morphology with additional abnormal intrasubstance signal.
Mildly increased intrasubstance PCL signal at the femoral attachment suggestive of low-grade sprain.
The mildly increased signal within the deep band of the MCL is suggestive of a low-grade sprain.
Case Discussion
Avulsion injuries of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) are uncommonly encountered.
In adults, ACL tears commonly occur in the mid-substance. In children, it has been hypothesized that there is a relative weakness of incompletely ossified bone relative to ligamentous fiber strength.
If an ACL avulsion fracture occurs it most commonly avulses from its tibial attachment with femoral ACL avulsions rare.
It is unknown whether this patient went on to have surgery and internal fixation of the displaced fragment.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.