Presentation
Recent diagnosis of lung carcinoma. Confusional state. Hyponatremia.
Patient Data
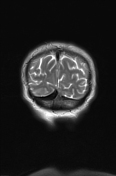

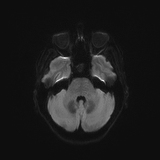


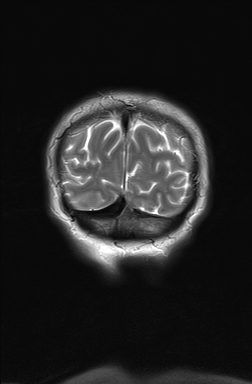
Abnormal swelling and signal hyperintensity of the left hippocampus on T2-weighted and FLAIR MRI sequences. No restricted diffusion in the DWI. Scattered white matter areas of high T2/FLAIR signal, suggestive of chronic small vessel ischemia.
CSF study. Microscopic description
Moderate pleocytosis with lymphoid predominance. No atypical cells were seen.
Neuroimmunology
Neuronal nuclear antibodies in CSF.
A strong band corresponding to anti-Hu antibodies was detected by immunoblot.
Case Discussion
MRI showed hyperintensity and selective swelling of the left hippocampus. Considering the oncologic context (lung carcinoma) of the patient these findings are consistent with autoimmune limbic encephalitis that is confirmed in the CSF and neuroimmunology studies (anti-Hu antibodies).
Anti-Hu encephalitis corresponds to a group I of autoimmune encephalitis, which includes those produced by intracellular antigens. It carries a poor prognosis (in fact this patient died a few weeks after diagnosis), and in 75% of cases, it is associated with lung cancer.
Differential diagnosis
- viral encephalitidies (herpes simplex virus more commonly)
- limbic encephalitidies
- seizure-related increased signal




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.