Presentation
Patient presenting to the emergency department with headache and bilateral papillary edema.
Patient Data



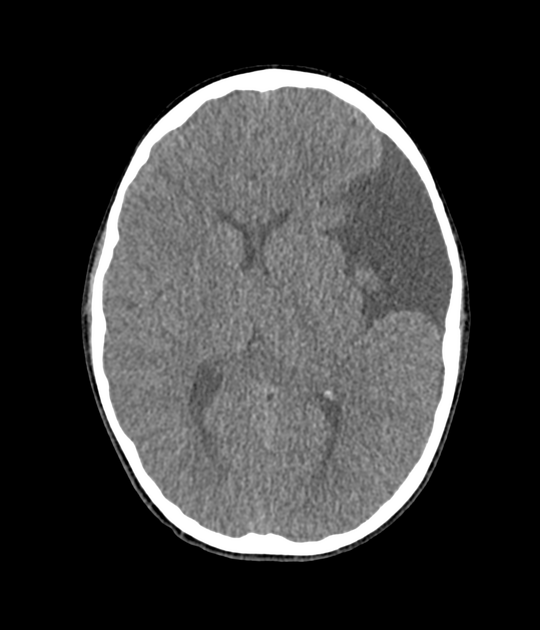
No signs of acute intra- or extra-axial hemorrhage.
A large fluid density extra-axial lesion centered in the left frontotemporal region is consistent with an arachnoidal cyst. It exerts mass effect on the ipsilateral frontal and temporal lobes, with a midline shift to the right of 3mm.
There is also anterior bulging of the posterior wall of both sclerae associated with an increase in the diameter of the optic nerves, consistent with the bilateral papillary edema observed in the physical examination.
The rest of the brain parenchyma, cerebellar and brainstem have no significant densitometric alterations.
Ventricular and cisternal system are mildly distorted but otherwise normal.
Paranasal sinuses and mastoid cells appropriately pneumatized. Absence of pneumatization of the frontal sinuses.
Case Discussion
This case shows a typical arachnoid cyst. It is located in the left middle cranial fossa, causing invagination and widening of the ipsilateral Sylvian fissure.
This case corresponds to type III according to Galassi's classification.
This case is submitted in collaboration with Dr. Adrià Roset Altadill




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.