Presentation
Obstructive Jaundice.
Patient Data
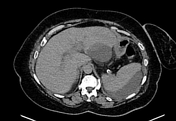

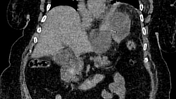

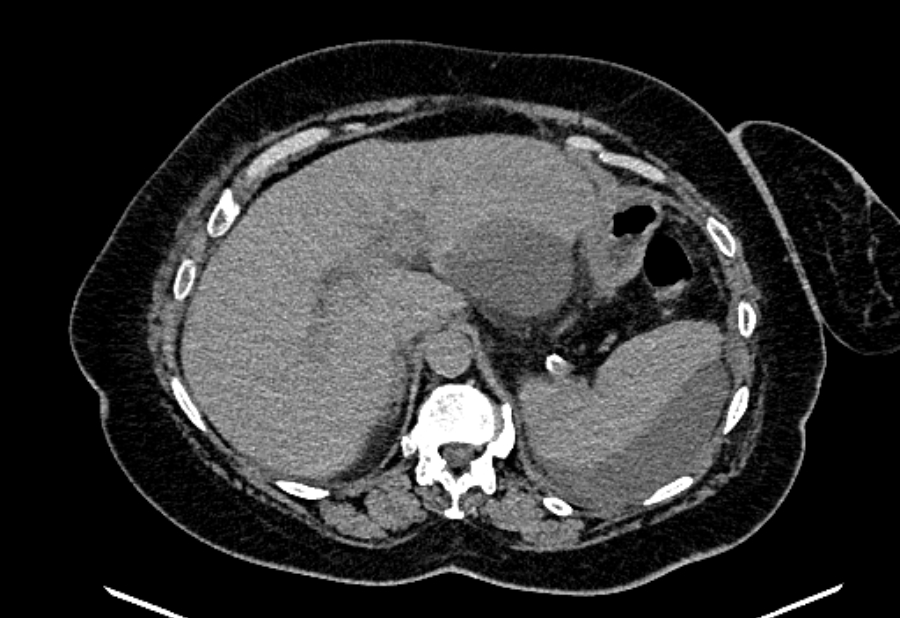
Non-contrast CT of the abdomen revealed:
- moderate to marked dilatation of both intra and extrahepatic radicles
- dilated CBD reaching 20 mm, with two distal hyperdense obstructing stones
- average size of the pancreas with mild interstitial edematous changes and minimal peripancreatic fat stranding
- multiple encysted peri-pancreatic peritoneal collections mainly at perisplenic space, lesser sac and gastro-hepatic ligament
- minimal left basal pleural effusion
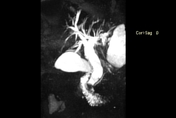

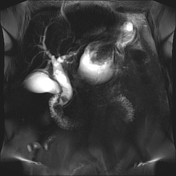

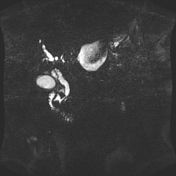

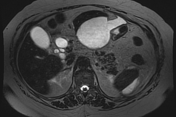

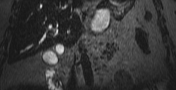

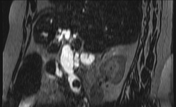




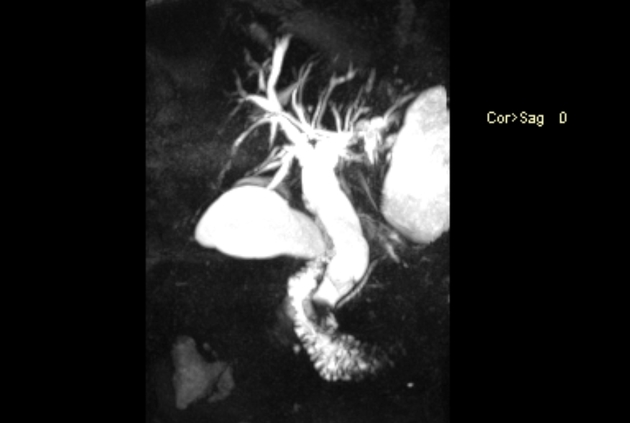
Moderate to marked dilatation of both intra and extrahepatic radicles, (CBD =20 mm), with two distal CBD obstructing stones, the larger measures 17 mm.
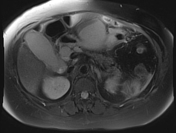
Multiple encysted peri-pancreatic peritoneal collections are seen mainly at peri-splenic space, lesser sac and gastro-hepatic ligament; the latter is largest measuring 10 cm in longest axial diameter.
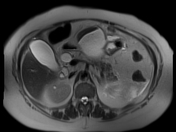
Thickening of the left lateroconal fascia, still the pancreas shows normal MRI size and signal; Non dilated main pancreatic duct (MPD), likely interstitial edematous pancreatitis (IEP).
Normal configuration of the gall bladder with no luminal signal defects (minimal focal adenomyomatosis at neck and fundus).
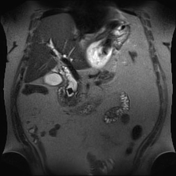
Basal chest scans revealed minimal left basal pleural effusion (sympathetic) and underlying relaxation atelectasis.
Case Discussion
The case shows features of choledocholithiasis with resultant extrahepatic biliary obstruction and complicated by acute interstitial edematous pancreatitis (biliary pancreatitis), which then also complicated by multiple peripancreatic fluid collections.
Choledocholithiasis is a common cause of acute pancreatitis (biliary pancreatitis).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.