Presentation
Brought to the emergency department, having been found unconscious in the bathroom of his house.
Patient Data

Bilateral low-density areas within the globus pallidus and diffuse, low attenuation changes within the cerebral white matter.
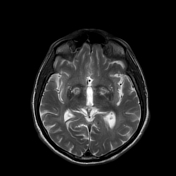

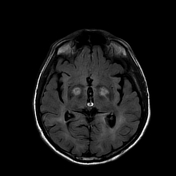

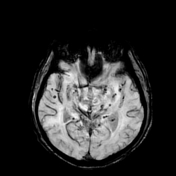

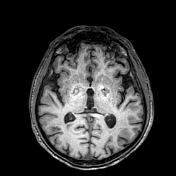

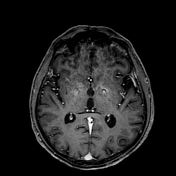


Exam performed 2 weeks later shows bilateral high signal intensities in the globus pallidus on T2/FLAIR sequences with peripheral enhancement after contrast administration.
Diffuse, bilateral and symmetric high signal intensities are visible in the white matter, also in the substantia nigra are visible bilateral high signal intensities.
Multiple, widespread focal regions of susceptibility induced signal loss are observed in the areas of basal ganglia, temporal lobes, pons, parahippocampal gyrus and occipital lobes representing hemosiderin deposits.
Case Discussion
The leak in a gas water heater was suspected. In the ER, the patient was unconscious and the COHb level was elevated.
Imaging studies, especially brain MRI, have demonstrated high sensitivity for detecting brain abnormalities after carbon monoxide poisoning. The most frequently affected areas are the brain regions with higher levels of iron (which are targeted by carboxyhemoglobin): the basal ganglia (especially the globus pallidus), and the substantia nigra.
Bilateral and symmetric lesions involving the globus pallidus suggest systemic or metabolic causes.
Differential diagnosis includes:
- toxic poisoning
- methanol: necrosis of the putamen may be observed, white matter edema may occur
- cyanide: also affects the cortex, putamen involvement
- metabolic abnormalities
- hepatic cirrhosis: bilateral hyperintense areas also in the substantia nigra
- Wilson disease: putaminal involvement, ventrolateral thalamus;
- hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: severe affects the cerebral cortex and hippocampi




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.