Presentation
Recurrent difficulty in breathing, asymptomatic most of the time.
Patient Data






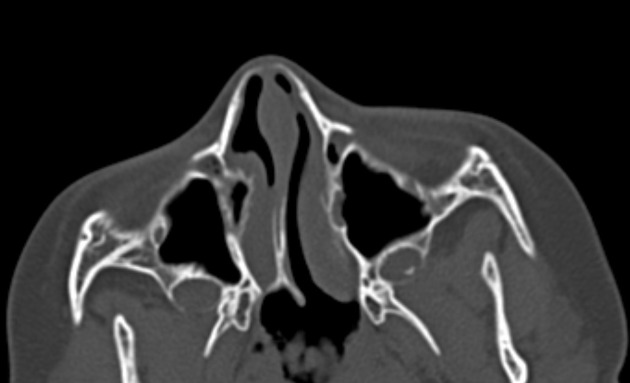
Narrowing of the right posterior chonana with convergence of its bony walls including the posterior segment of the bony nasal septum and bony bridge completely obstructs its aperture. This is associated with retained secretions and mucosal thickening of the right compartment of nasal cavity. Consequent secondary widening of the left sided posterior choana is noted.
Case Discussion
Choanal atresia usually presents in neonates. It is one of the commonest causes of nasal obstruction in neonates and infants. It is more commoner in females and unilateral. Unilateral choanal atresia present late and can be asymptomatic or present with rhinorrhea while bilateral atresias can present with neonatal respiratory distress. Osseous obstruction of the posterior choana is the most common type (90%).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.