Presentation
Right-sided pyramidal and extrapyramidal features, early postural instability with falls, cerebellar, and dystonic speech - symptom onset 5 years ago.
Patient Data
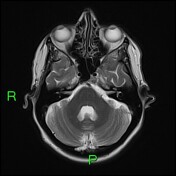

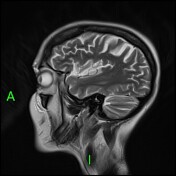

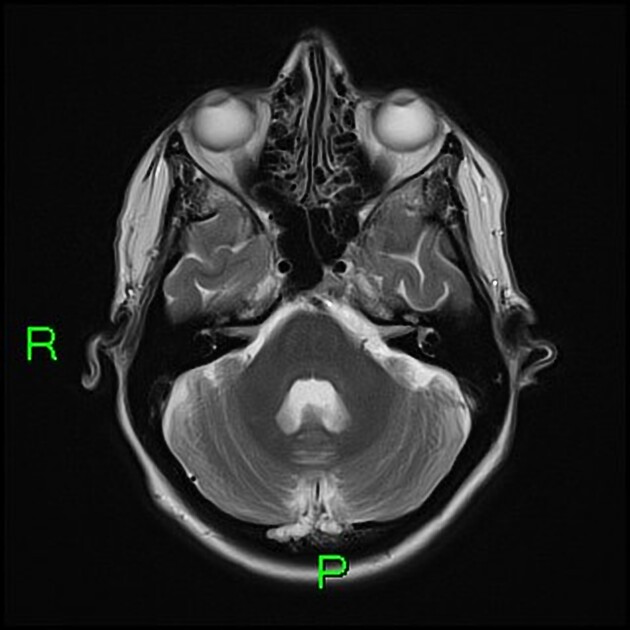
Initial MRI brain showed disproportionate volume loss towards the vertex, predominately affecting the parietal lobes but also the frontal lobes and also there is cerebellar volume loss to a lesser degree. The temporal lobe volumes were normal.
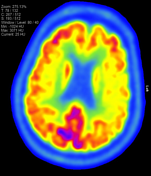


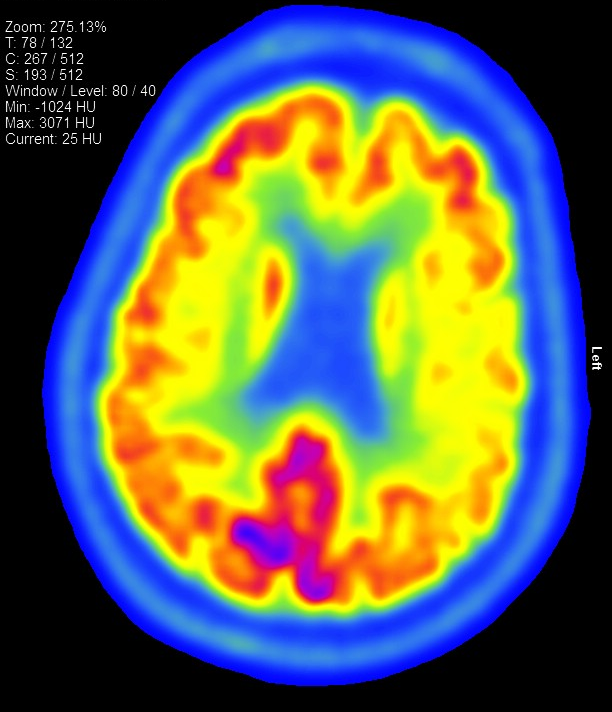
An F18-FDG PET CT performed 1 year later showed areas of relative hypometabolism, most pronounced in the left sensorimotor strip and left posterior frontal cortex in the superior/middle gyri but also seen along the left superior parietal cortex.
There is mild/moderate hypometabolism in the left putamen, mild hypometabolism in the left thalamus compared to the normal right, and possibly subtle asymmetrical hypo metabolism in the left caudate.
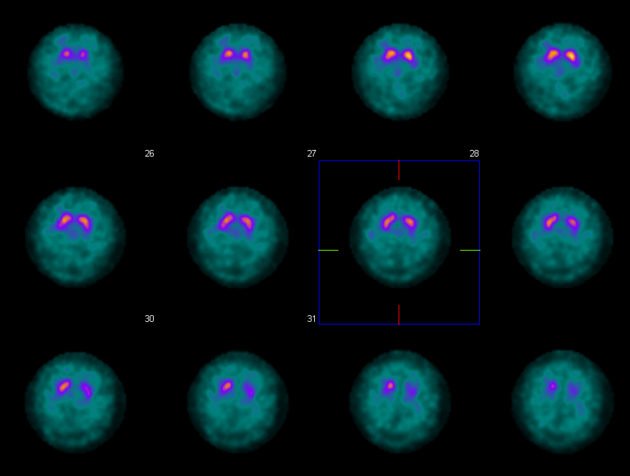
A DAT (dopamine transport) scan performed a few months after the PET CT showed severe loss of tracer uptake in the left putamen and slight/mild loss in the left caudate. The uptake in the right striatum appeared visually normal.
Case Discussion
The FDG PET CT shows abnormal asymmetrical hypometabolism in the left sensory motor/posterior frontal cortex associated with further hypometabolism in the left basal ganglia and thalamus. Combined with the loss of dopamine transporter function in the left striatum on the DAT scan and the anatomical changes on the initial MRI, the overall imaging appearances are compatible with corticobasal degeneration.
Genetic testing for spinocerebellar ataxia 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, and 17 was negative. Vitamin E and screening for Wilson's disease and cerebellar ataxia were also negative.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.