Presentation
A known diabetic patient presented with sudden onset of fever and headache.
Patient Data
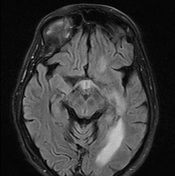

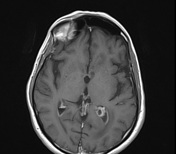

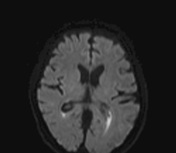

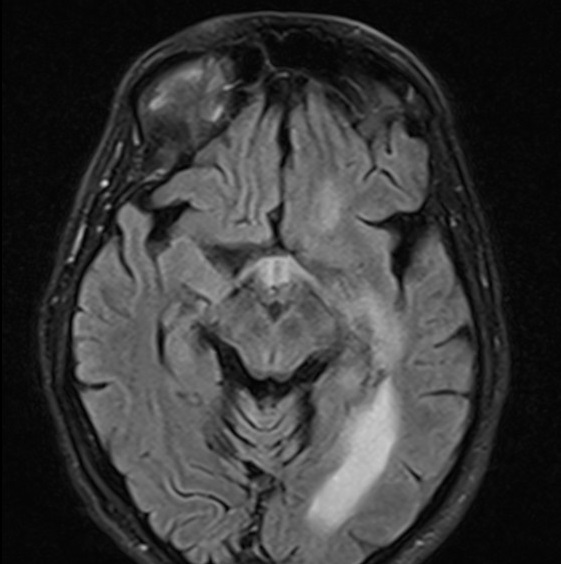
There is subependymal periventricular hyperintensity along the walls of the lateral and third ventricles on the T2 (not shown) and FLAIR sequences. The ventricular walls show diffusion restriction. The choroid plexus and ventricular walls show contrast enhancement. There is no basal meningeal contrast enhancement. The rest of the brain MRI is normal.
The features are consistent with ventriculitis.
Case Discussion
This particular patient's CSF analysis revealed raised cryptococcal antigen and positive India ink staining. Blood culture was positive for Cryptococcus neoformans. HIV screening was negative. He was managed with intravenous amphotericin. The clinical and radiological features are consistent with cryptococcal ventriculitis.
Cryptococcus neoformans is an encapsulated yeast that mainly affects the central nervous system. CNS cryptococcosis is common in HIV-AIDS patients, much less so in immunocompromised patients due to other etiologies (e.g. diabetes). CNS cryptococcosis may manifest as meningitis, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, and ventriculitis.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.