Presentation
Nephrotic syndrome with normal ultrasound of the kidneys.
Patient Data
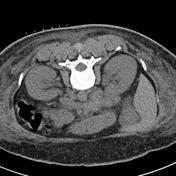

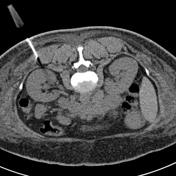



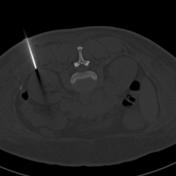

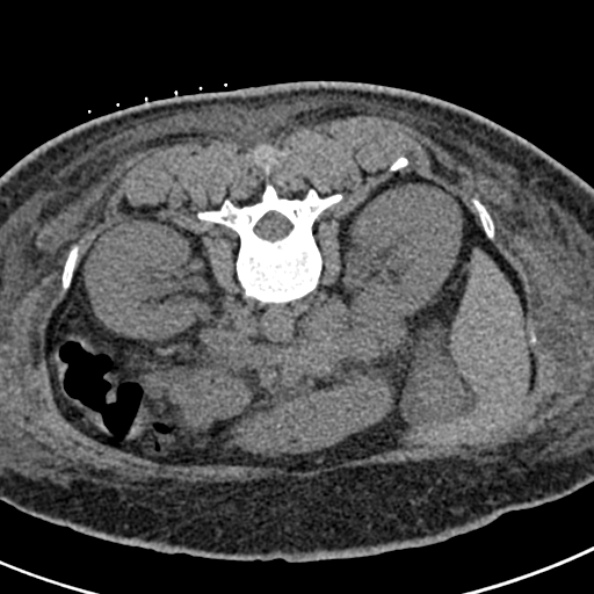
The patient's body habitus did not permit ultrasound guided biopsy.
The steps for CT guided renal biopsy: skin surface markers to choose site, following by infiltration needle and co-axial needle position prior to biopsy.
1. Local anesthetic infiltration needle - to check position and aid angulation planning for co-axial needle.
2. Co-axial needle 'parked' in the ideal position prior to a 2cm biopsy core acquisition.
3. Bone windows allow for more accurate assessment of needle tip position, as artifact from needle reduced.
Case Discussion
CT guided non-focal renal biopsy for assessment of intrinsic renal pathology.
Ultrasound is most commonly used as truly dynamic and non-radiation required.
In larger patients CT guidance is required.
Note the angulated approach from the lateral position to prevent traversing paraspinal muscle.
As two cores are required, a co-axial needle - usually 18G - is used.
The other cortex is particularly targeted to acquire a large number of glomeruli.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.