Presentation
Left loin/flank pain and recurrent urinary tract infection. Ultrasound revealed left parapelvic renal cyst
Patient Data
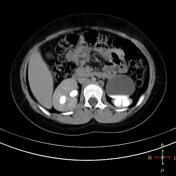

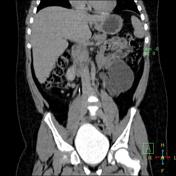




A fairly large cystic lesion is related to the anterior aspect of left kidney. In delayed images, it appears connected to the renal calyces and filled with contrast. The ureter could be identified arising from the inferior aspect of this cyst. Also there is moderate left hydronephrosis with parenchymal thinning and no contrast seen at left ureter suggesting PUJ obstruction.
Diagnosis: Extrarenal pelvis with PUJ obstruction and moderate hydronephrosis.
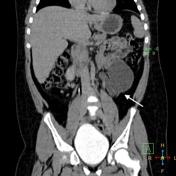
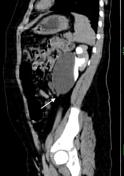
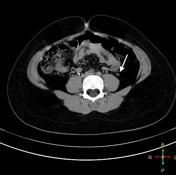

The ureter could be identified arising from the inferior aspect of this cyst (white arrows).
Case Discussion
The diagnosis of PUJ obstruction wasn't easy on US due to the narrow connections between the calyces and extra renal pelvis and so para pelvic cyst compressing the ureter and cause hydronephrosis was the original diagnosis.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.