Patient Data
Age: 55 years
Gender: Female




Download
Info
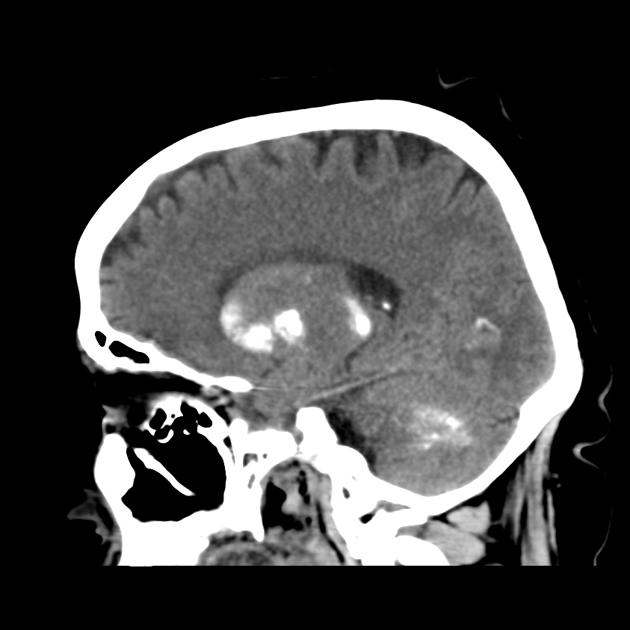
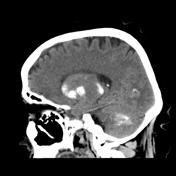
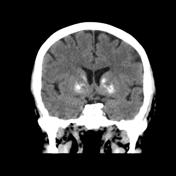
Unenhanced CT show shows bilateral calcifications, slightly asymmetrical in the basal ganglia and the thalamus, also the dentate nucleus are calcified.
Case Discussion
Bilateral striopallidodentate calcinosis (BSPDC), commonly known as Fahr disease, is a rare syndrome characterized by symmetrical calcification of the basal ganglion and dentate nucleus. The basal ganglia are the most common site of involvement. Most cases present with extrapyramidal symptoms initially.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.