Presentation
An otherwise healthy man presented with progressive psychosis.
Patient Data
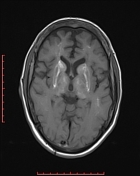

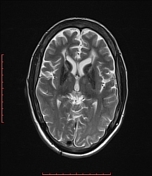

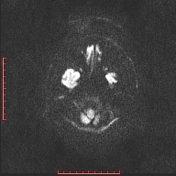

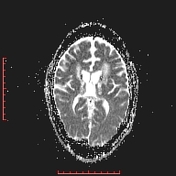

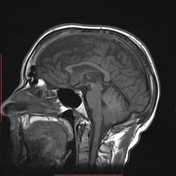

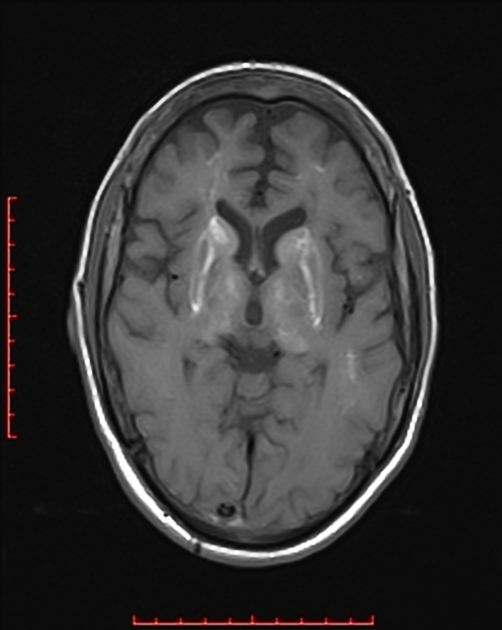
There are bilateral symmetrical signal changes in the caudate, lentiform nuclei, thalami, dentate and red nuclei as well as the subcortical white matter, mostly increased signal on T1W images and decreased signal on T2W images. There is no restricted diffusion in the affected areas, but b0 images demonstrate some blooming artifact.
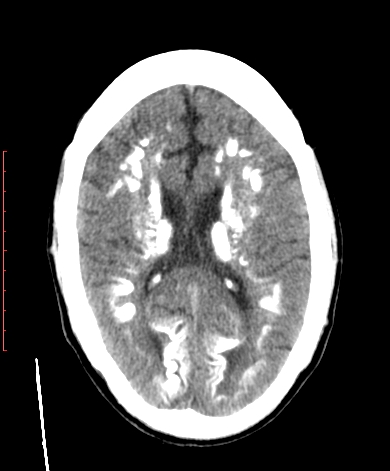
Axial brain CT scan images demonstrate bilateral symmetrical calcification in the caudate, lentiform nuclei and thalami, dentate and red nuclei and subcortical white matter.
Case Discussion
Fahr disease, also known as familial cerebral ferrocalcinosis, is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by calcification in the deep grey matter nuclei, and subcortical white matter.
Patients usually present clinically in the 5th and 6th decades with psychological and motor disorders.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.