Presentation
Cognitive impairment.
Patient Data
Age: 65
Gender: Male
Download
Info
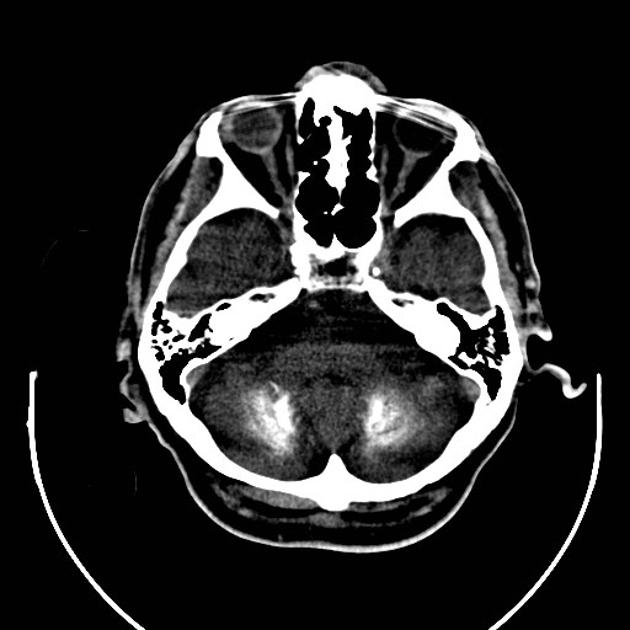
Extensive and bilateral calcification on basal ganglia, thalami, subcortical white matter and dentate nuclei of the cerebellum.
Case Discussion
Fahr disease is a disorder characterized by abnormal calcium deposition with subsequent atrophy involving the basal ganglia +/- cerebral and cerebellar cortical regions.
Calcification is found primarily in the globus pallidus, but putamen, caudate, thalamus, dentate nucleus, corona radiata and subcortical white matter can also be affected.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.