Presentation
Abdominal pain of unknown origin
Patient Data


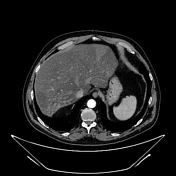

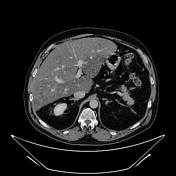

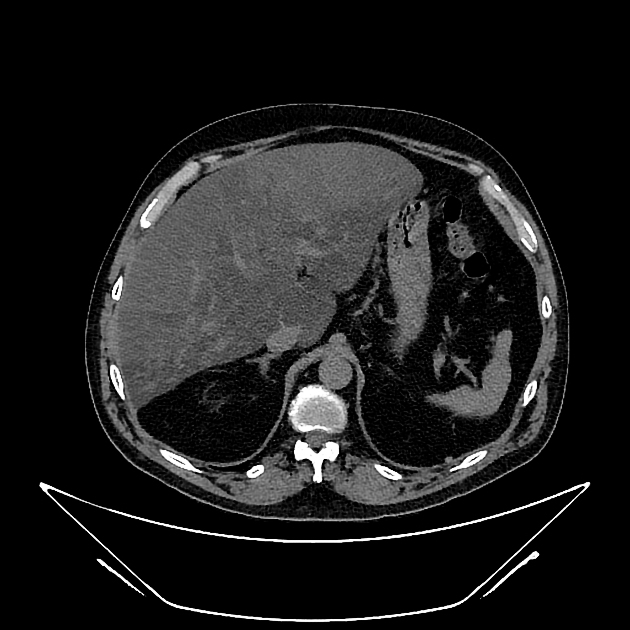
Unenhanced and C+ CT imaging demonstrate irregular liver areas of constantly decreased attenuation consistent with fat infiltration, alternating with regions of normal homogenous parenchymal density keeping with focal fat sparing.
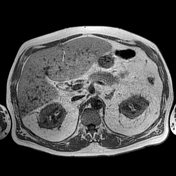

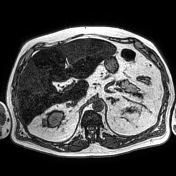

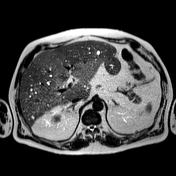

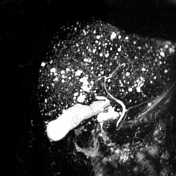
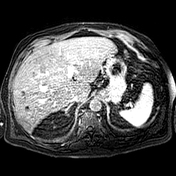

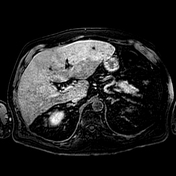


MR shows large hepatic regions of intense signal drop on the opposed phase image, indicative of fat within the hepatocytes, alternating precontrast sequence homogeneous parenchymal areas with delayed biliary excretion at 20 minutes.
Millimetric multiple liver cysts with ubiquitous distribution.
Non-dilatation of intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary tracts.
Case Discussion
Cross-sectional studies show multifocal areas of fat deposits alternating with regions of fat sparing within the liver parenchyma. The irregularity of the different areas resembles the border lines drawn on a geographical map 1. The introduction of hepatospecific contrast medium is relevant because fat-sparing areas demonstrate delayed biliary excretion, as they have more functioning hepatocytes than fat-rich areas.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.