Presentation
Delayed mental and motor milestones. History of severe birth asphyxia.
Patient Data


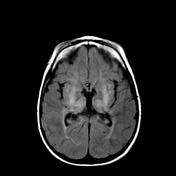

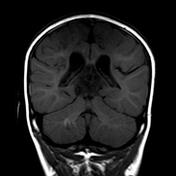

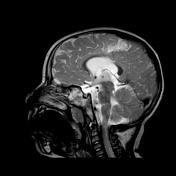



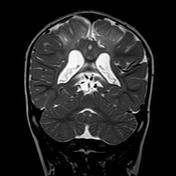

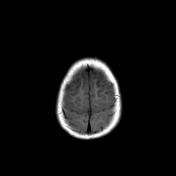

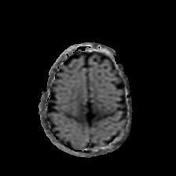

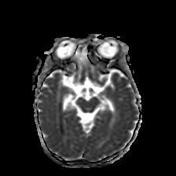

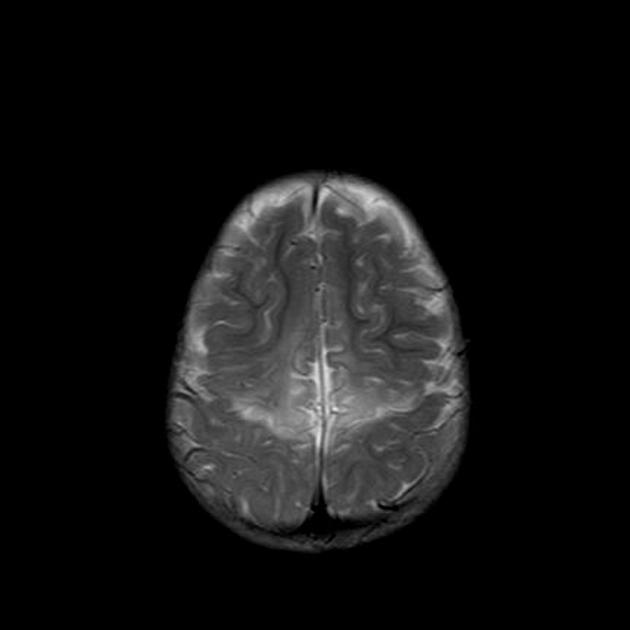
Bilateral hyperintense signals are seen at basal ganglia, thalami, and perirolandic cortex.
Case Discussion
Severe asphyxia in term neonates results in an injury involving the deep gray matter (putamina, ventrolateral thalami, hippocampi, dorsal brainstem, and lateral geniculate nuclei) and occasionally the perirolandic cortex.
These areas of the brain are actively myelinating (an energy-intensive process) or contain the highest concentrations of NMDA receptors at term and are, therefore, the most susceptible to neonatal hypoxic-ischemic insult.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.