Presentation
Chest pain and palpitations.
Patient Data
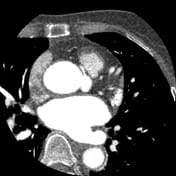

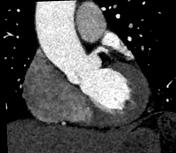

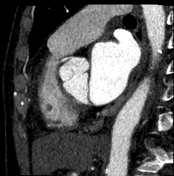

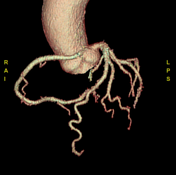

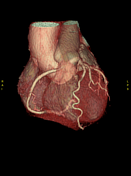

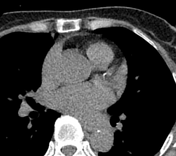

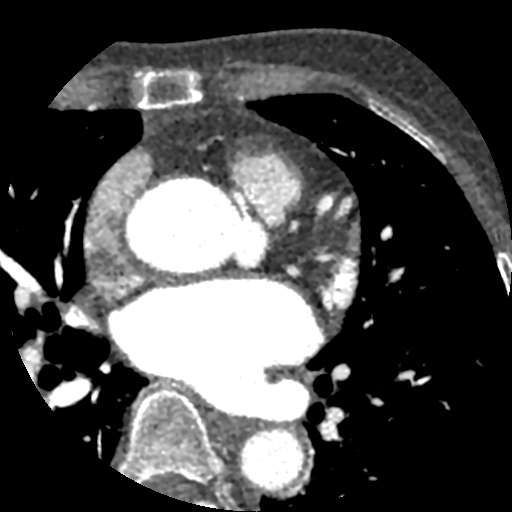
Calcium score: 8.
Calcified atherosclerotic plaque causing mild stenosis of the left anterior descending artery.
The right coronary artery (RCA) has an aberrant origin from the left coronary sinus, coursing between the ascending aorta and the pulmonary trunk, consistent with an interarterial course of the RCA, causing approximately 50–60% stenosis at the proximal segment of the RCA, without associated atherosclerotic plaque or calcification.
Case Discussion
The imaging findings are consistent with an interarterial course of the right coronary artery.
This represents a rare anomalous course of the coronary artery, associated with a potential risk of myocardial ischemia, and is therefore also referred to as a malignant course of the right coronary artery.
During physical activity or exertion, the aorta and pulmonary artery may dilate, potentially compressing the RCA as it courses between them. This can lead to reduced myocardial perfusion, resulting in ischemia, arrhythmias, or even sudden cardiac death.
AHA/ACC 2020 guidelines4: surgery is class I recommendation for AAOCA with symptoms and documented myocardial ischemia.
Surgical correction is the primary treatment approach in cases where:
there are clear symptoms such as chest pain or exertional syncope
there is evidence of myocardial ischemia on imaging studies (e.g., CMR, stress testing, SPECT)
the RCA demonstrates a high-risk interarterial course
Surgical techniques include:
unroofing: enlargement of the intramural segment between the anomalous artery and the aortic wall
reimplantation: re-establishing the origin of the coronary artery to the appropriate sinus
coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): used selectively in certain cases
stenting or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): not considered a first-line treatment option. Its role remains limited and under investigation, and it is not widely recommended in current clinical guidelines
Case co-author: consultant specialist Tran Quyet Thang, Military Hospital 175, Vietnam.
Images were processed by radiologic technologist Nguyen Van Tuan, Military Hospital 175, Vietnam.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.