Presentation
Pain at the dominant wrist. No history of trauma.
Patient Data


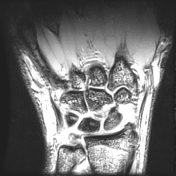

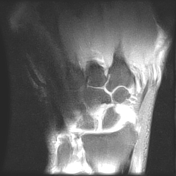

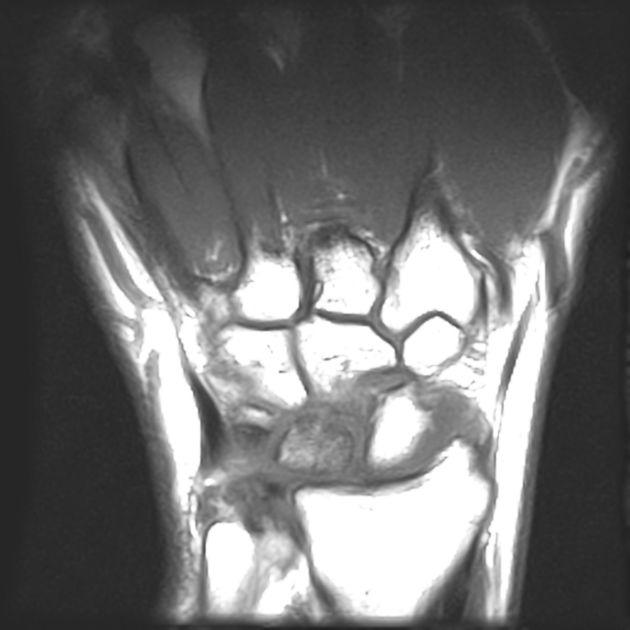
Diffusely decreased signal intensity is present within the lunate bone on the T1W images and heterogeneously increased signal on T2W images (Stage II Kienbock disease). There is slight loss of lunate height as well, predominantly on its radial side. No scapholunate dissociation.
Negative ulnar variance with compensatory thickening of the triangular fibrocartilage is also present.
Small wrist joint effusion is noted.
Unremarkable flexor and extensor tendons.
Case Discussion
Kienbock disease is the eponymous name given to avascular necrosis (aseptic necrosis) involving the lunate. Typical MRI findings include:
- sclerosis (low T1 and T2) centrally and within the radial aspect of lunate
- bone edema (high T2, intermediate T1) may be seen in the acute phase, particularly on the radial side
- 75% of cases are associated with negative ulnar variance
There are several important causes of abnormal lunate signal on MRI, the most frequent causes being Kienbock disease (25%), ulnar impaction syndrome (25%), and intra-osseous ganglia (20%).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.