Presentation
Headache and deterioration of the level of consciousness. No vomiting, upper or lower limb weakness
Patient Data
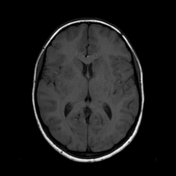

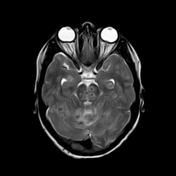

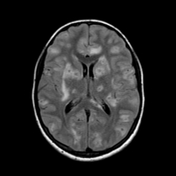

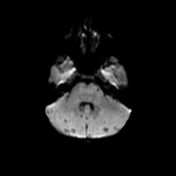



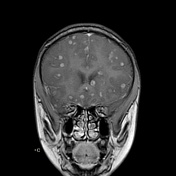

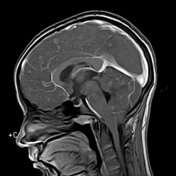

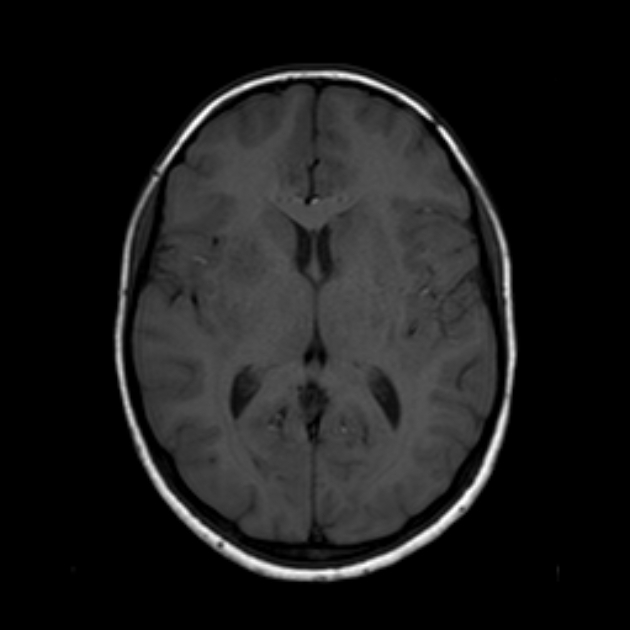
Innumerable small size (+/- 1 cm) focal lesions are seen scattered all over the brain involving the cerebral hemispheres, brainstem and cerebellum. The lesions are isointense on T1 and have low intensity center on T2/FLAIR with peripheral hyperintensity and surrounding edema. No significant mass effect. They show marked ring enhancement after contrast administration.
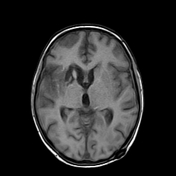

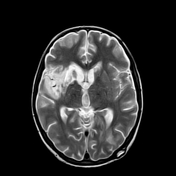

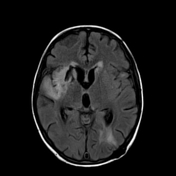

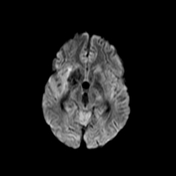

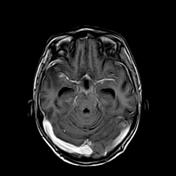

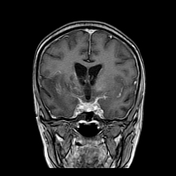

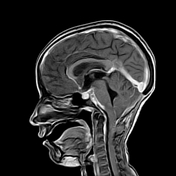

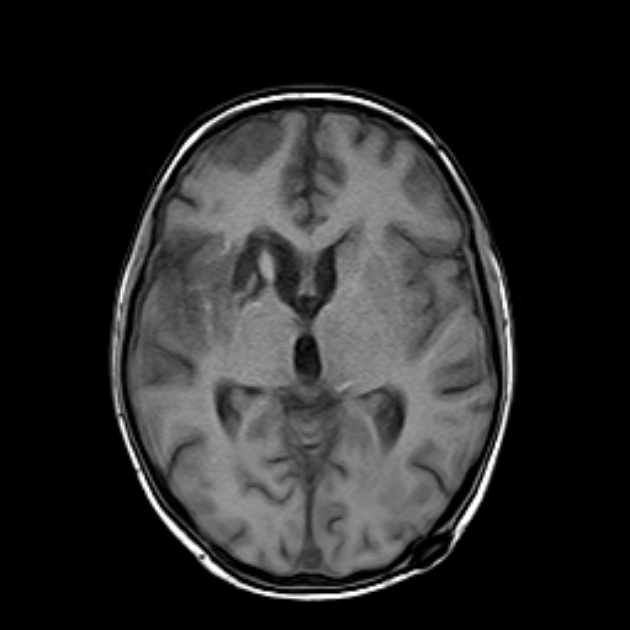
This study was done 4 months later under umberella of TB therapy. There is almost near total resolution of the scattered focal lesions however the patient developed basal meningitis as shown by thickened enhancing meningeal lining at the suprasellar cistern and clivus with associated communicating hydrocephalus. Moreover there is right basal ganglionic old infarction at MCA territory mostly from arteritis.
Case Discussion
After successful antituberculous therapy the clinical diagnosis of miliary TB of the brain was made. The patient was found immunosuppressed and tuberculin negative. Other focal lesions were found at the spleen and liver. There is increased incidence of arterial infarction in case of basal meningitis specially in children.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.