Presentation
Right upper quadrant pain.
Patient Data
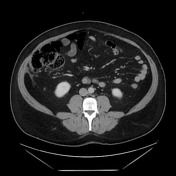

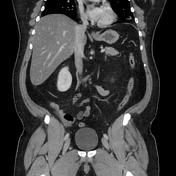

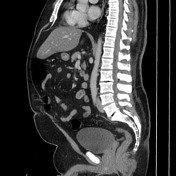

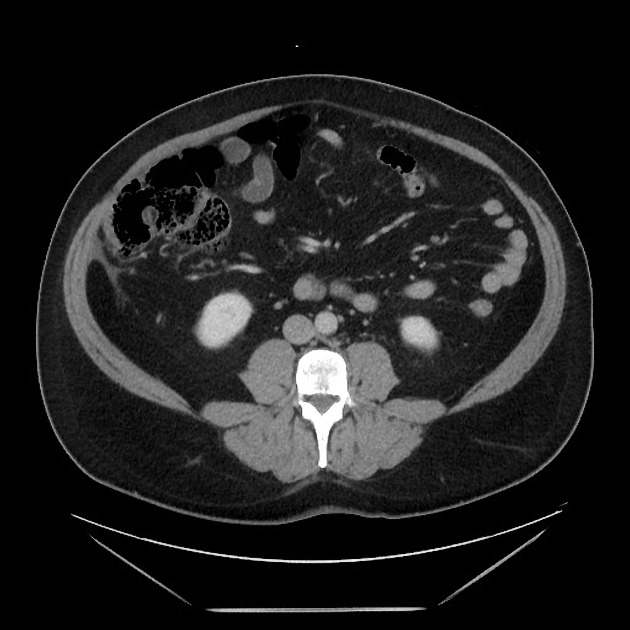
Hepatic steatosis.
Oval fat-containing mass in the right upper quadrant anterior to the inferior right hepatic lobe, with minimal surrounding fluid. Minimal reactive thickening of the hepatic flexure. Most apparent on coronal images.
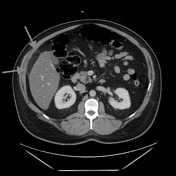
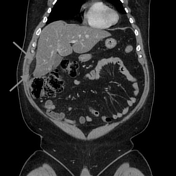
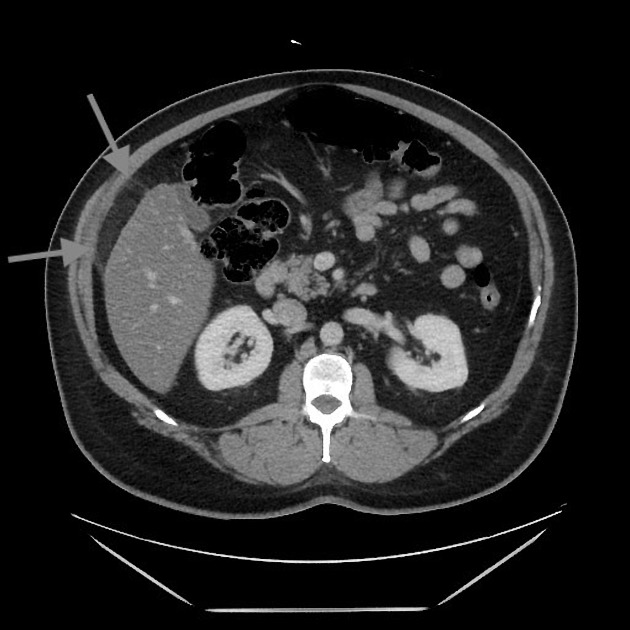
Note the relatively subtle appearance on axial, with more well-defined boundaries on the coronal images.
Case Discussion
Acute self-limited ischemia of the fat (omental infarct/epiploic appendagitis) is an important diagnosis to keep in mind when reading contrast CT and flank pain studies, as it can mimic other causes of acute abdominal pain. This case of omental infarct occurred in the more typical location (right abdomen) and is relatively subtle on the axial images, but more well-defined on the coronal images. The small amount of surrounding fluid and fluid in the paracolic gutter help confirm the acute presentation with some associated inflammation, accounting for the patient's pain.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.