Presentation
Neonate. Premature third born. Craniofacial stigmata are syndromic.
Patient Data
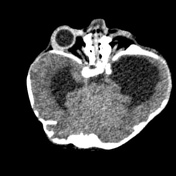

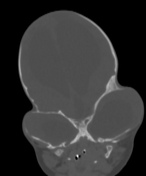

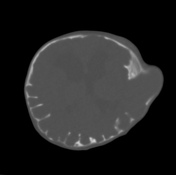

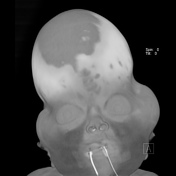
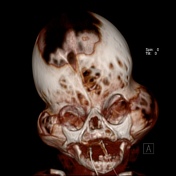
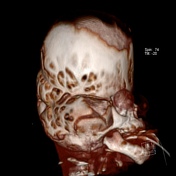
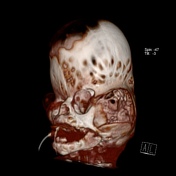
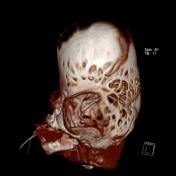
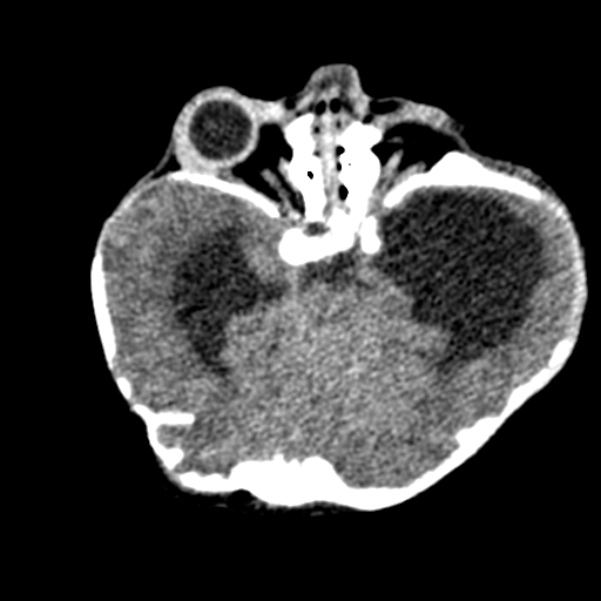
Grossly abnormal craniofacial appearances, the most pronounced being turicephaly.
All of the calvarial sutures are prematurely fused.
Non ossification of multiple areas in the skull ( hence the incomplete 3D reconstructions )
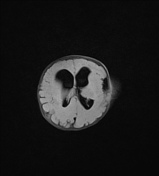
Bony spiculations protruding between the cerebral sulci.
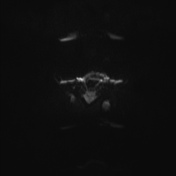
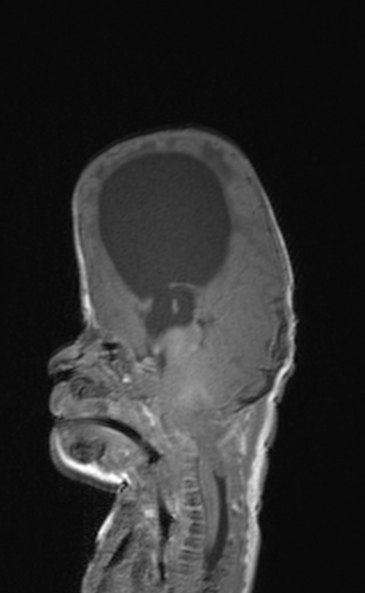
Failure of formation of supraorbital ridges with resultant gross proptosis.
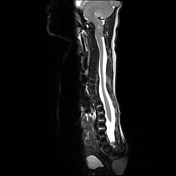
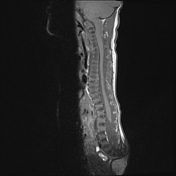
Small posterior fossa with cerebellar tonsillar herniation.
Hydrocephalus with transependymal edema.
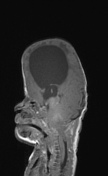

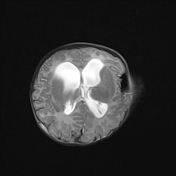

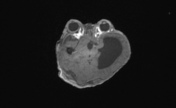









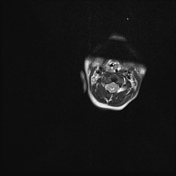

Non ossified skull vault bilaterally close to the vertex and in the inferior temporal bones, especially on the left with dural protrusion.
Hypertelorism. Severe bilateral proptosis ( due to shallow orbits ).
Biventricular hydrocephalus, with disproportionate temporal horn dilatation. Minor amount of transependymal edema.
Small posterior fossa with marked cerebellar tonsillar herniation ( to the C2/C3 junction ) with cord remodeling at the foramen magnum.
Case Discussion
Craniofacial syndromes are a collection of the most severe forms of congential craniofacial abnormalities, believed to result from a failure in the degree of migration of mesenchyme to the skull base and face.
The syndromes include: Crouzon, Apert, Coffin-Lowry and Pfeiffer's.
Many of the abnormalities between the syndromes are common, such as proptosis, hypoplastic sinuses and calvarial thinning. The features vary with the sutural craniosynostoses.
Features of Pfeiffer's syndrome include:
- cloverleaf brain
- proptosis and hyperteleorism
- calvarial thinning with or without a pseudoencephalocele
- small posterior fossa with cerebeller tonsilar herniation
- bony spiculation
- turcephaly - due to premature closure of the coronal, sagittal and lambdoid sutures




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.